Wrong selection between a level switch and transmitter can lead to process failures, safety hazards, and unnecessary costs.
Level switches provide binary (on/off) signals at specific points, while level transmitters continuously measure and transmit actual level values across a range.
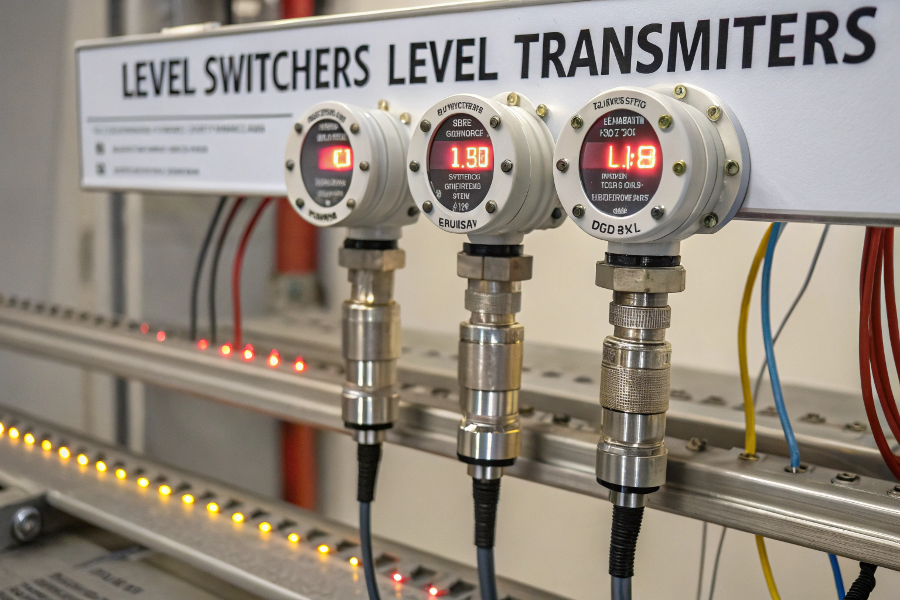

Level Switches vs Level Transmitters
Let me share my expertise from numerous level measurement installations and applications.
What is the Difference Between a Switch and a Transmitter?
Many customers struggle with choosing between switches and transmitters for their applications.
Switches provide discrete (on/off) output at set points, while transmitters offer continuous measurement signals across their range, typically 4-20mA or digital outputs.
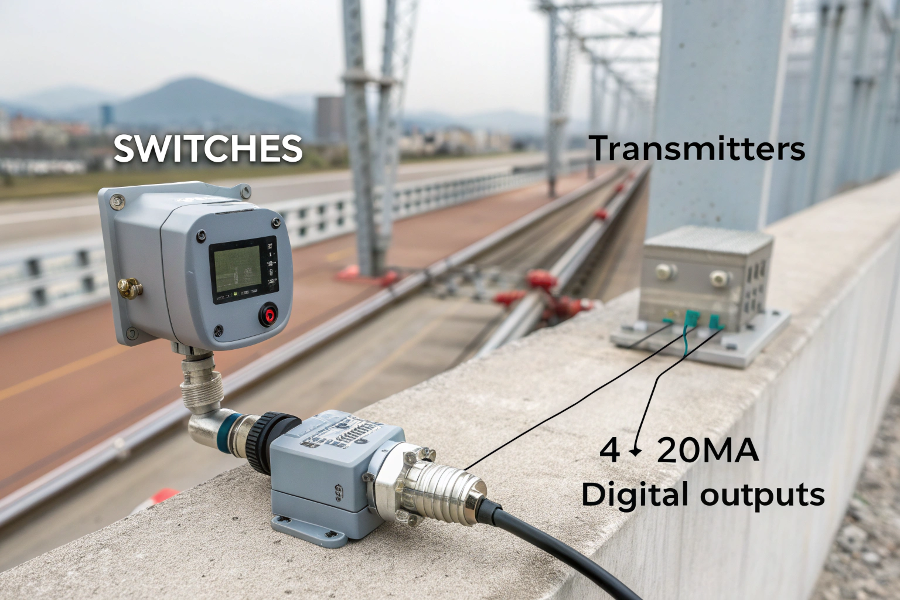

Switch vs Transmitter Operation
From my field experience:
Key Differences
Operational Characteristics
Feature Switch Transmitter Output Binary Continuous Signal Contact/Digital Analog/Digital Application Point Level Continuous Level Cost Lower Higher Selection Factors
- Process requirements
- Safety needs
- Budget constraints
- Control strategy
Application Considerations
Installation Requirements
- Mounting options
- Power needs
- Signal interface
- Environmental protection
Maintenance Aspects
- Calibration needs
- Testing frequency
- Reliability factors
- Life expectancy
These insights help in making informed decisions.
What is a Level Switch?
Misunderstanding level switch operation can result in tank overflow or dry run conditions.
A level switch is a device that detects when liquid or solid material reaches a specific point, providing an on/off signal for control or alarm purposes.
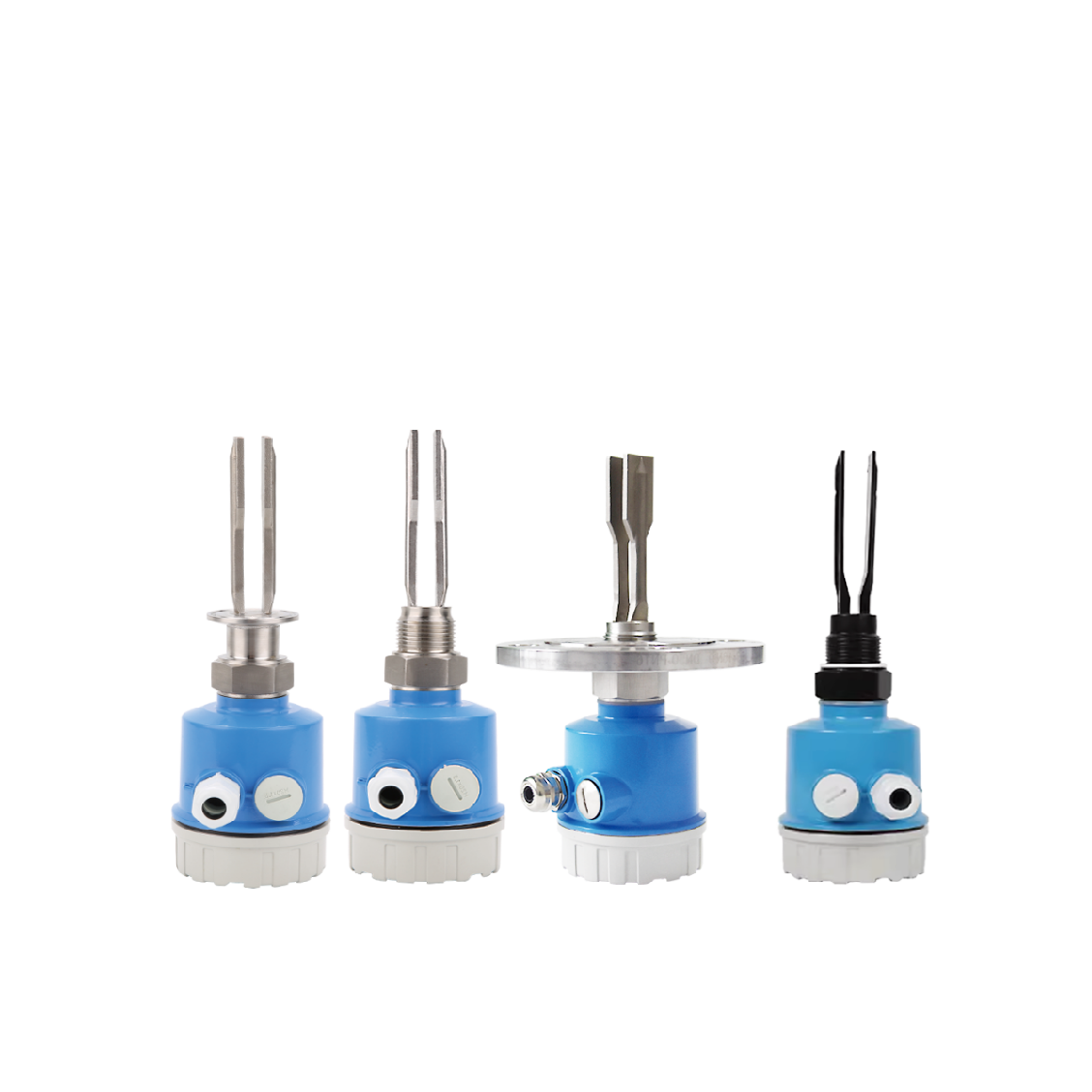

Level Switch Types and Applications
Based on my switch installation experience:
Switch Technologies
Common Types
Type Principle Best Application Float Buoyancy Clean liquids Vibrating Resonance Powder/Granules Capacitive Dielectric Interface/Solids Optical Light reflection Clear liquids Operating Principles
- Physical movement
- Material properties
- Electronic sensing
- Mechanical action
Implementation Guidelines
Selection Criteria
- Process material
- Operating conditions
- Safety requirements
- Environmental factors
Installation Considerations
- Process connection
- Switch position
- Electrical connection
- Maintenance access
These factors ensure reliable switch operation.
What is a Level Transmitter?
Selecting the wrong level transmitter type can result in inaccurate measurements and process inefficiencies.
A level transmitter is a device that continuously measures and transmits level information, providing real-time data for process monitoring and control.
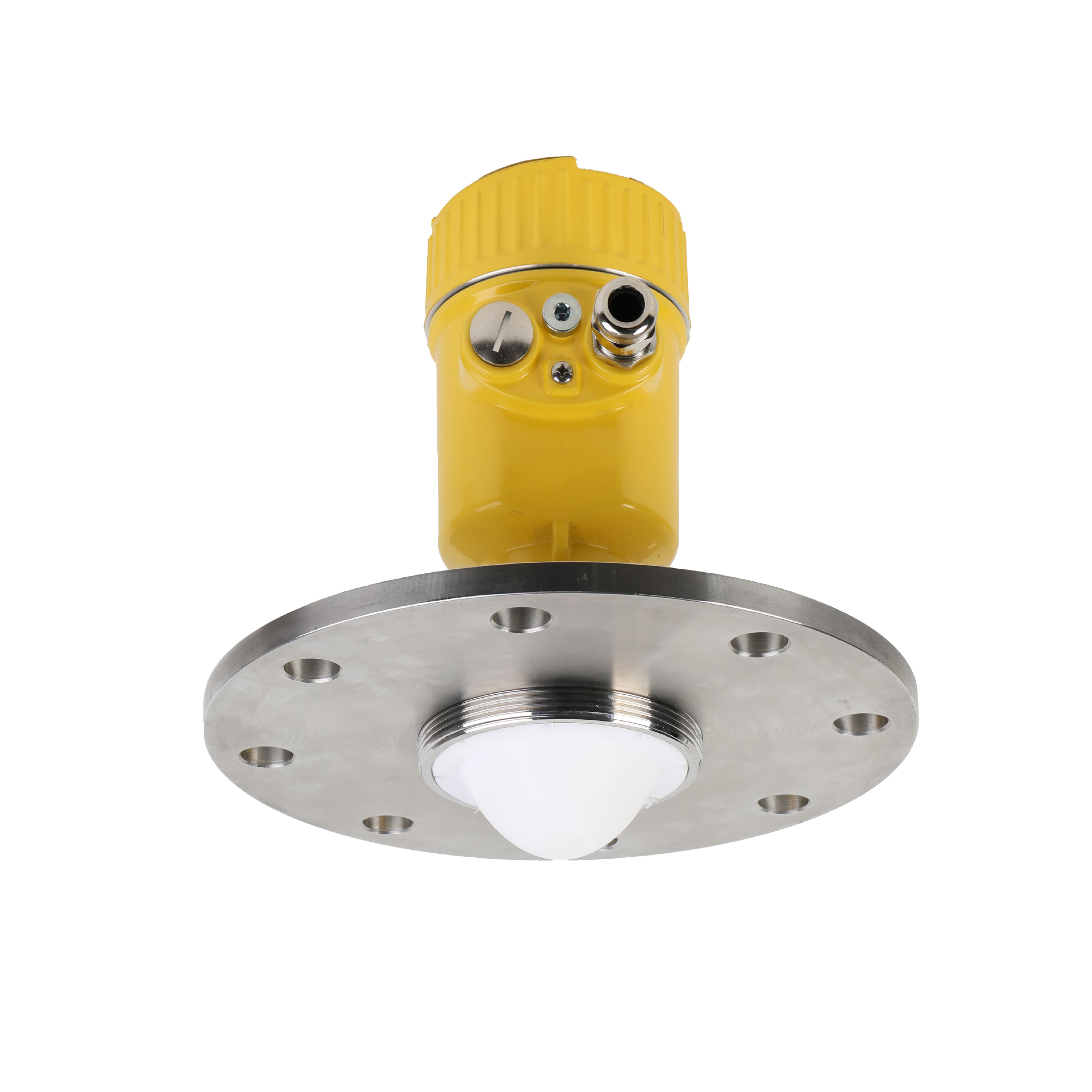

Level Transmitter Technologies
Drawing from my transmitter implementation experience:
Transmitter Technologies
Measurement Methods
Type Principle Best Use Pressure Hydrostatic Open tanks Radar Microwave Closed vessels Ultrasonic Sound waves Open channels Guided Wave TDR Interface Performance Factors
- Accuracy needs
- Range requirements
- Process conditions
- Environmental effects
Application Guidance
Selection Process
- Material properties
- Vessel conditions
- Accuracy requirements
- Budget constraints
Implementation Steps
- Proper sizing
- Correct mounting
- Signal integration
- Calibration procedure
These considerations ensure optimal performance.
What is the Primary Function of a Level Switch?
Using level switches incorrectly can compromise process safety and equipment protection.
The primary function of a level switch is to provide reliable point-level detection for process control, equipment protection, and safety system operation.
Level Switch Functions
From my safety system experience:
Primary Functions
Critical Applications
Function Purpose Example Overfill Prevention High alarm Dry run Protection Pump control Interface Detection Separation Safety Shutdown Emergency stop Control Functions
- Process automation
- Alarm indication
- Equipment protection
- Inventory control
Implementation Strategy
Safety Considerations
- Failure modes
- Response time
- Redundancy needs
- Testing requirements
Maintenance Requirements
- Regular testing
- Performance verification
- Documentation
- Spare parts
These functions ensure safe and reliable operation.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between level switches and transmitters is crucial for selecting the right device for your application, ensuring safe and efficient process control.



