Engineers often struggle to find accurate, reliable flow measurement solutions that don’t interfere with the process.
Transit time ultrasonic flow meters measure flow by calculating the difference in time for ultrasonic signals traveling with and against the flow direction, providing accurate non-invasive measurement.
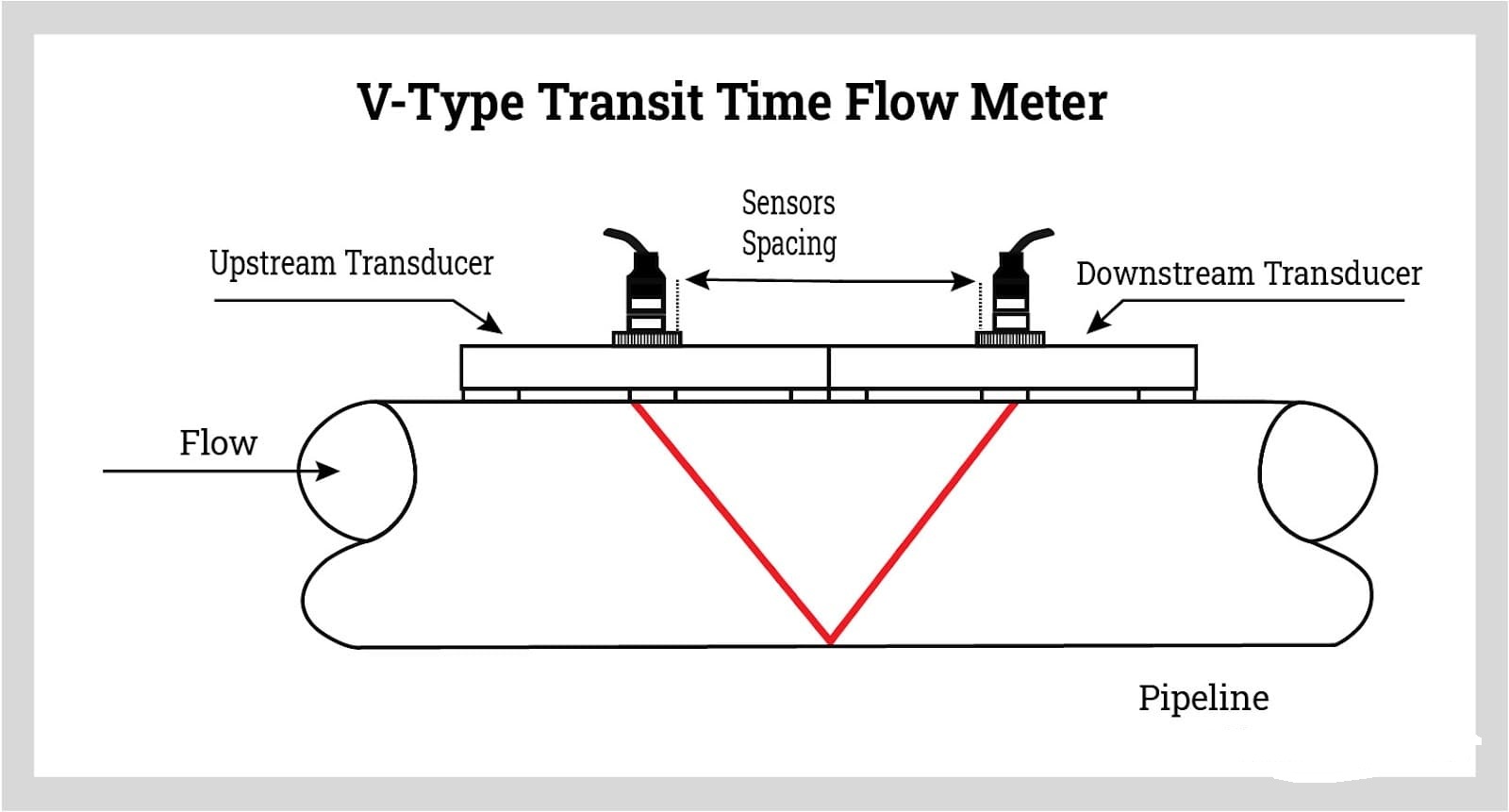
Transit Time Measurement Principle
Let me share what I’ve learned from implementing these systems across various industries.
What is Ultrasonic Flowmeter Transit Time?
Plant operators frequently ask about the working principle behind transit time technology.
Transit time ultrasonic flow meters use two transducers to send and receive ultrasonic signals, measuring the time difference caused by fluid flow to calculate flow rate.
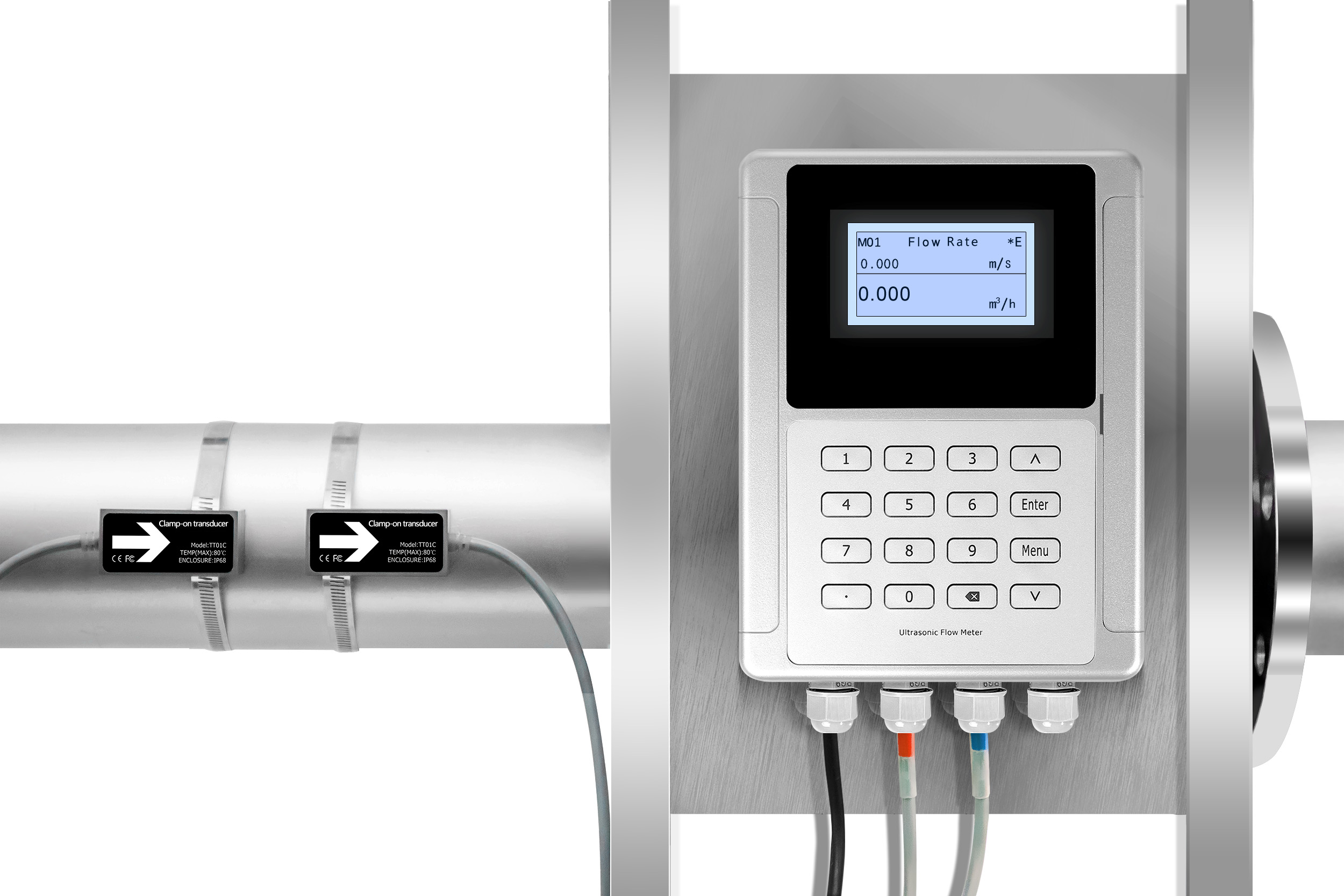

Transducer Setup and Signal Path
From my design experience:
Operating Principle
Signal Path Components
Element Function Impact Upstream transducer Signal emission Time measurement Downstream transducer Signal reception Flow calculation Fluid medium Signal transmission Accuracy Pipe wall Signal passage Installation Measurement Process
- Signal generation
- Time difference calculation
- Flow velocity computation
- Rate conversion
Technical Implementation
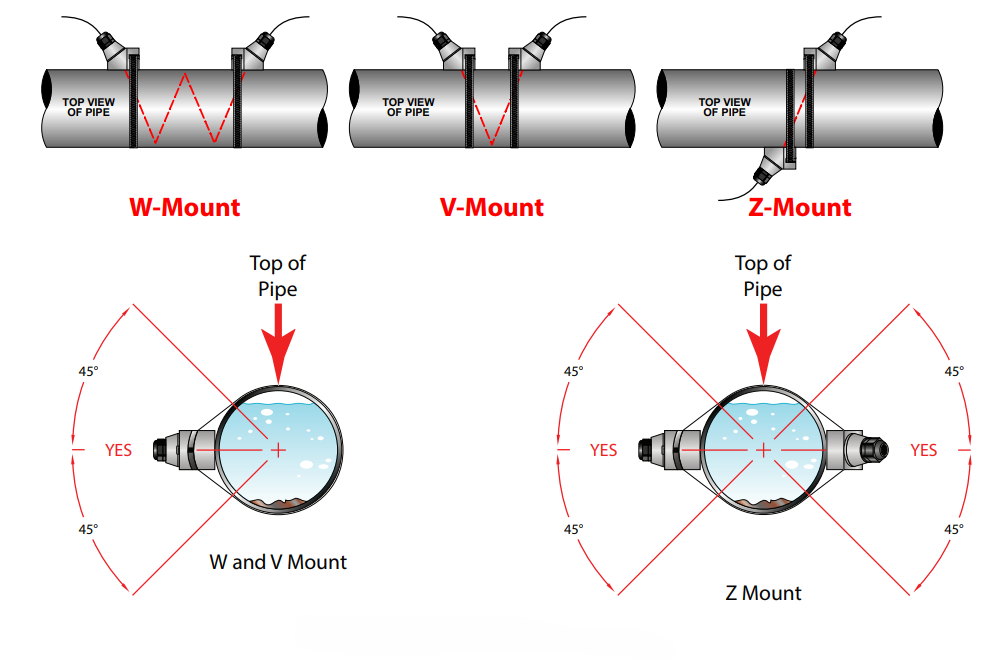
Installation Configuration
- Single path setup
- Dual path arrangement
- Multiple path systems
- Mounting options
Signal Processing
- Digital conversion
- Noise filtering
- Signal validation
- Data processing
What is the Response Time of the Ultrasonic Flow Meter?
Users need to understand how quickly their meters can detect flow changes.
Modern transit time ultrasonic flow meters typically respond within 1 second, with some high-performance models achieving response times as fast as 100 milliseconds.

Response Time Characteristics
Based on my testing experience:
Response Characteristics
Time Factors
Parameter Range Application Update rate 10-100 Hz Process control Response time 0.1-1 second Batch operations Settling time 1-5 seconds Stable reading Damping User-adjustable Signal stability Performance Impact
- Flow conditions
- Signal strength
- Processing speed
- Filter settings
Application Considerations
Critical Parameters
- Process requirements
- Control system needs
- Signal quality
- Environmental factors
Optimization Methods
- Filter adjustment
- Signal processing
- Installation quality
- Parameter tuning
What are the Limitations of Ultrasonic Flow Meters?
Engineers must understand technology constraints for proper application.
Ultrasonic flow meters face challenges with highly aerated fluids, low flow conditions, and require minimum straight pipe runs for accurate measurement.

Flow Meter Limitations
Drawing from my field experience:
Technical Limitations
Physical Constraints
Limitation Impact Solution Air content Signal loss De-aeration Straight run Flow profile Proper installation Pipe condition Signal quality Surface preparation Temperature Accuracy Compensation Application Restrictions
- Flow range limits
- Fluid properties
- Installation space
- Environmental conditions
Performance Challenges
Measurement Issues
- Low flow accuracy
- Signal attenuation
- Installation effects
- Temperature drift
Operating Constraints
- Power requirements
- Maintenance needs
- Calibration intervals
- Environmental protection
What is Transit Time Measurement?
Process engineers need to understand the fundamental principle behind this technology.
Transit time measurement is the process of calculating flow velocity by measuring the difference in time it takes ultrasonic signals to travel upstream versus downstream in a fluid.
Transit Time Measurement Process
Based on my implementation experience:
Measurement Process
Signal Propagation
Phase Action Purpose Emission Signal generation Time reference Transmission Fluid passage Flow interaction Reception Signal detection Time measurement Processing Data analysis Flow calculation Calculation Methods
- Time difference
- Velocity determination
- Flow rate conversion
- Total flow computation
System Components
Hardware Elements
- Transducers
- Signal processors
- Display units
- Communication interfaces
Software Features
- Signal analysis
- Data processing
- Output configuration
- Diagnostic tools
Conclusion
Transit time ultrasonic flow meters offer reliable, non-invasive flow measurement when properly applied, with understanding of their capabilities and limitations being key to successful implementation.



