Keeping your electromagnetic flow meter in top condition ensures accurate measurements and long service life. These devices may not have moving parts, but they still need proper care.
Electromagnetic flow meters require periodic electrode cleaning, verification of ground connections, and diagnostic checks to maintain accuracy. Preventive maintenance typically includes visual inspections every 3 months and full calibration annually.

Flow Meter Maintenance Procedures
Modern flow meter maintenance goes beyond just fixing problems when they occur. Let’s examine the complete maintenance picture.
What Is the Maintenance of Electromagnetic Flow Meter?
Routine maintenance prevents small issues from becoming big problems during critical operations.
Regular maintenance involves cleaning electrodes1, checking liners for wear, verifying electrical connections, and ensuring proper grounding. These simple steps can prevent 80% of common flow meter problems.
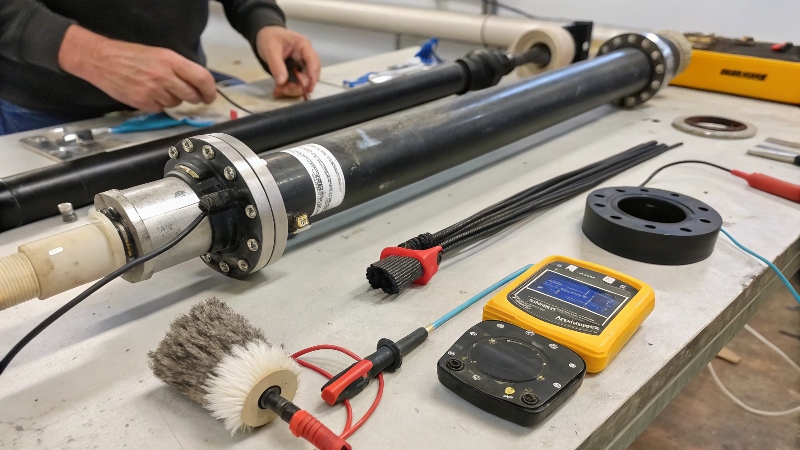

Flow Meter Component Maintenance
Maintenance procedures vary by model and application, but all follow the same basic principles:
Essential Maintenance Tasks
| Task | Frequency | Tools Needed | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrode Cleaning | 3-6 months | Soft brush, cleaning fluid | Maintains signal quality |
| Ground Verification | Monthly | Multimeter | Prevents measurement errors |
| Liner Inspection | Annually | Flashlight, magnifier | Avoids leaks and damage |
| Calibration Check | 6-12 months | Reference flow standard | Ensures measurement accuracy |
| Cable Inspection | Quarterly | Visual check | Prevents signal interference |
With industry moving toward smart monitoring systems, many users now integrate maintenance alerts2 with their SCADA systems for proactive care.
What Is the Preventive Maintenance of a Flow Meter?
Preventive maintenance helps avoid unplanned downtime and measurement inaccuracies.
A comprehensive preventive maintenance program for electromagnetic flow meters includes scheduled inspections, cleaning cycles, performance verifications, and documentation of all service activities to establish maintenance history.

Flow Meter Preventive Maintenance
Breaking down preventive maintenance into systematic steps ensures nothing gets overlooked:
Preventive Maintenance Protocol3
Scheduled Inspections (Monthly)
- Check for physical damage
- Verify proper mounting
- Inspect electrical connections
Cleaning Procedures
- Electrode cleaning (acidic/alkaline solutions depending on buildup)
- Junction box moisture check
- Cable connection cleaning
Performance Verification
- Zero calibration check
- Span check against known flow rates
- Signal quality verification
Documentation
- Record all maintenance activities
- Note any abnormal conditions
- Track performance trends
Modern flow meters increasingly include self-diagnostics to support these preventive measures, reducing manual checking requirements.
How Do You Maintain a Flow Meter?
Proper maintenance combines scheduled tasks with condition-based monitoring for optimal performance.
Effective flow meter maintenance requires following manufacturer guidelines while adapting to specific process conditions, implementing both scheduled servicing and real-time monitoring of meter health indicators.

Step-by-Step Flow Meter Maintenance
Maintenance best practices evolve with technological advances:
Maintenance Optimization Techniques
- Track electrode resistance trends
- Monitor signal-to-noise ratio
- Analyze power supply stability
Predictive Maintenance
- Use smart meter diagnostics
- Implement IoT-enabled monitoring
- Analyze historical performance data
Proper Cleaning Methods
- Ultrasonic cleaning for heavy buildup
- Chemical cleaning matched to deposits
- Mechanical cleaning for stubborn cases
Calibration Management
- Field verification vs. lab calibration
- Maintaining traceable standards
- Documentation of calibration history
The industry shift toward Industry 4.0 is transforming maintenance from calendar-based to condition-based approaches.
What Are the Requirements for a Magnetic Flow Meter?
Meeting all installation and operational requirements ensures trouble-free service.
Magnetic flow meters require proper grounding, compatible fluid conductivity, correct pipe sizing, and appropriate material selection for wetted parts to function reliably in industrial environments.
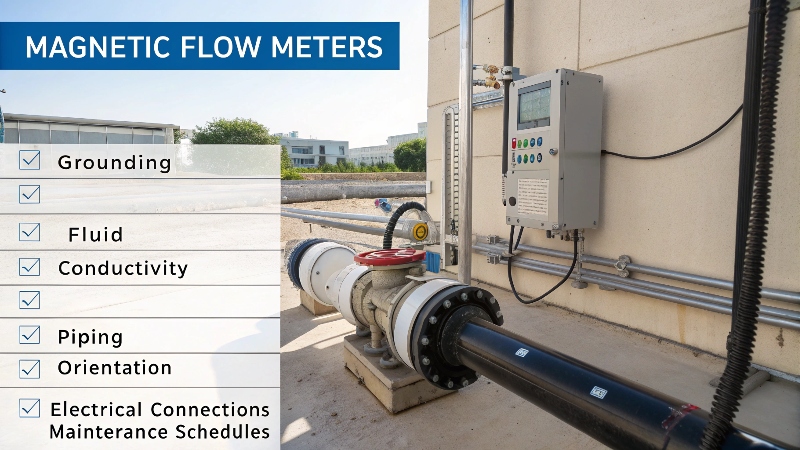
Magnetic Flow Meter Requirements
Understanding all operational requirements prevents performance issues:
Comprehensive Requirements Checklist
Installation Requirements:
- Proper grounding rings or electrodes
- Adequate straight pipe runs (typically 5D upstream, 3D downstream)
- Correct orientation (vertical or horizontal per model)
- Proper support to avoid vibration
Operational Requirements:
- Minimum fluid conductivity5 (usually 5 μS/cm)
- Compatible fluid temperature range
- Appropriate pressure rating
- Proper liner material for fluid compatibility
Environmental Requirements:
- Protection from extreme weather
- Proper electrical enclosure rating
- Adequate space for maintenance access
- Protection from mechanical damage
The growing emphasis on predictive maintenance means modern systems need built-in diagnostic capabilities meeting new industry standards.
Conclusion
Modern electromagnetic flow meters require systematic maintenance including cleaning, inspection and calibration, with industry trends moving toward smart monitoring and predictive maintenance strategies.
Proper cleaning of electrodes is vital for accurate flow measurement. Learn effective cleaning techniques to enhance performance. ↩
Discover how integrating maintenance alerts with SCADA systems can improve operational efficiency and reduce downtime. ↩
Understanding the Preventive Maintenance Protocol can help ensure effective maintenance practices and avoid costly downtimes. ↩
Explore this link to understand how Condition-Based Monitoring can enhance maintenance efficiency and reduce downtime. ↩
Understanding the minimum fluid conductivity is crucial for ensuring system efficiency and preventing performance issues. ↩



