When industrial processes lack accurate pressure monitoring, they risk equipment damage, safety hazards, and inefficient operations.
Pressure transmitters are essential instruments that measure and convert pressure into standardized electrical signals, commonly used in industrial processes for monitoring, control, and safety applications.

Pressure Transmitter Overview
I’ve worked with countless pressure measurement applications, and I’ll share what I’ve learned about maximizing their effectiveness.
What Are the Applications of Pressure Sensors?
Finding the right pressure sensor for your application can be overwhelming with so many options available.
Pressure sensors are widely used in manufacturing, process control, HVAC systems, and hydraulic systems to monitor pressure levels and ensure safe, efficient operations.

Pressure Sensor Applications
From my extensive field experience:
Industrial Applications
Process Industries
Industry Application Key Benefit Chemical Process Control Safety Oil & Gas Pipeline Monitoring Reliability Power Generation Boiler Protection Efficiency Water Treatment Pump Protection Longevity Manufacturing Uses
- Quality control
- Machine protection
- Process optimization
- System monitoring
Specialized Applications
Critical Functions
- Safety systems
- Leak detection
- Flow measurement
- Level calculation
Environmental Monitoring
- Weather stations
- HVAC systems
- Clean rooms
- Altitude measurement
These applications demonstrate the versatility of pressure sensing technology.
What is a Transmitter, its Type and Application?
Selecting the wrong transmitter type can lead to inaccurate measurements and system failures.
A transmitter is an instrument that converts physical measurements into standardized electrical signals, with types including pressure, temperature, flow, and level transmitters.

Different Types of Transmitters
Based on my technical knowledge:
Transmitter Categories
Common Types
Type Measurement Output Signal Pressure Force/Area 4-20mA Temperature Heat 4-20mA/Digital Flow Movement 4-20mA/Pulse Level Height 4-20mA Technology Options
- Smart transmitters
- Analog devices
- Digital outputs
- Wireless solutions
Application Considerations
Selection Criteria
- Accuracy needs
- Process conditions
- Installation requirements
- Communication protocol
Performance Factors
- Response time
- Stability
- Reliability
- Maintenance needs
These factors guide proper transmitter selection.
What is a Transmitter Used For?
Understanding transmitter applications helps optimize their use in process control systems.
Transmitters convert physical parameters into standardized signals for monitoring, control, and automation systems, enabling remote process monitoring and control.

Transmitter Applications
Drawing from my implementation experience:
Primary Functions
Process Control
Function Purpose Benefit Monitoring Data Collection Insight Control Process Management Efficiency Safety Protection Risk Reduction Quality Product Consistency Reliability System Integration
- DCS integration
- PLC connection
- SCADA systems
- Data logging
Implementation Benefits
Operational Advantages
- Remote monitoring
- Automated control
- Preventive maintenance
- Process optimization
Business Impact
- Cost reduction
- Quality improvement
- Safety enhancement
- Efficiency gains
These benefits justify transmitter implementation.
How Does a Pressure Transmitter Operate?
Proper understanding of pressure transmitter operation ensures optimal performance and maintenance.
Pressure transmitters use sensing elements like diaphragms to convert pressure into mechanical movement, then transform this into electrical signals through various technologies.
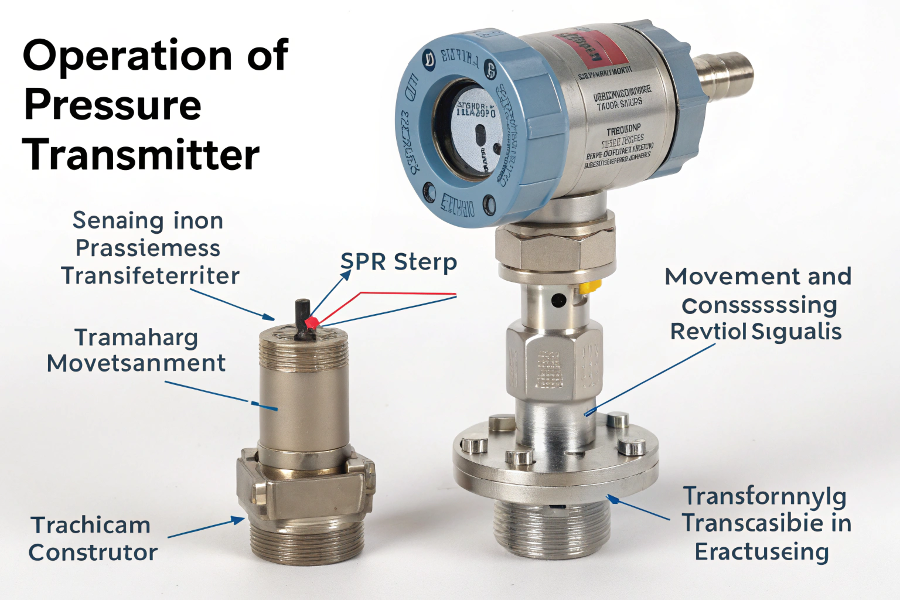
Pressure Transmitter Operation
Based on my technical expertise:
Operating Principles
Key Components
Component Function Role Sensor Pressure Detection Primary Electronics Signal Processing Secondary Housing Protection Support Connection Process Interface Interface Measurement Process
- Pressure input
- Mechanical deformation
- Signal generation
- Output transmission
Performance Aspects
Critical Parameters
- Accuracy rating
- Temperature effects
- Stability factors
- Response time
Environmental Impact
- Temperature variations
- Vibration effects
- EMI influence
- Moisture exposure
These factors affect measurement reliability.
Conclusion
Pressure transmitters are vital instruments for process control, offering accurate measurement and reliable operation when properly selected and installed for specific applications and conditions.



