Poorly maintained flow meters can cost thousands in inaccurate measurements and unexpected breakdowns.
Flow meter maintenance involves regular inspection, cleaning, calibration, and parts replacement to ensure accuracy and longevity, typically requiring scheduled checks every 6-12 months.

Flow Meter Maintenance Overview
Through my years of experience maintaining various flow measurement systems, I’ve developed comprehensive maintenance strategies.
What is the Maintenance of Flow Meter?
Neglecting flow meter maintenance can lead to costly measurement errors and system failures.
Flow meter maintenance includes visual inspections, cleaning, calibration verification, and component checks, following a structured schedule based on the meter type and application.
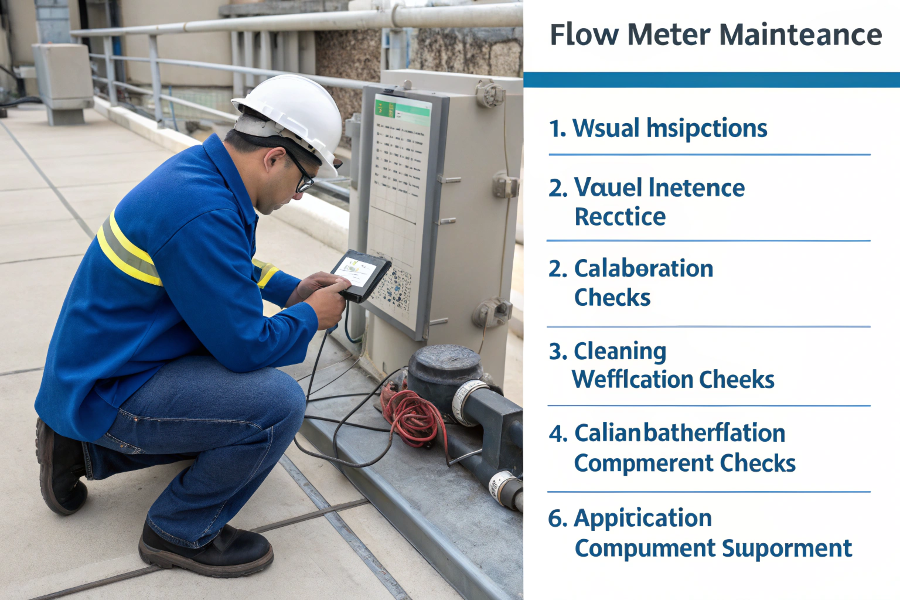
Flow Meter Maintenance Steps
From my maintenance experience:
Maintenance Procedures
Regular Tasks
Task Frequency Purpose Visual Inspection Monthly Detect issues early Cleaning Quarterly Prevent buildup Calibration Check Annually Ensure accuracy Parts Inspection Semi-annually Prevent failures Critical Checks
- Signal output verification
- Zero point validation
- Leak detection
- Electronics testing
Documentation Requirements
Maintenance Records
- Service dates
- Work performed
- Parts replaced
- Test results
Performance Tracking
- Accuracy trends
- Error patterns
- Repair history
- Calibration data
Proper maintenance ensures reliability.
What Material is Used for Flow Meter Liner?
Selecting the wrong liner material can result in premature wear and chemical compatibility issues.
Flow meter liners commonly use PTFE, PFA, ETFE, rubber, or ceramic materials, chosen based on the fluid properties, temperature, and chemical compatibility requirements.
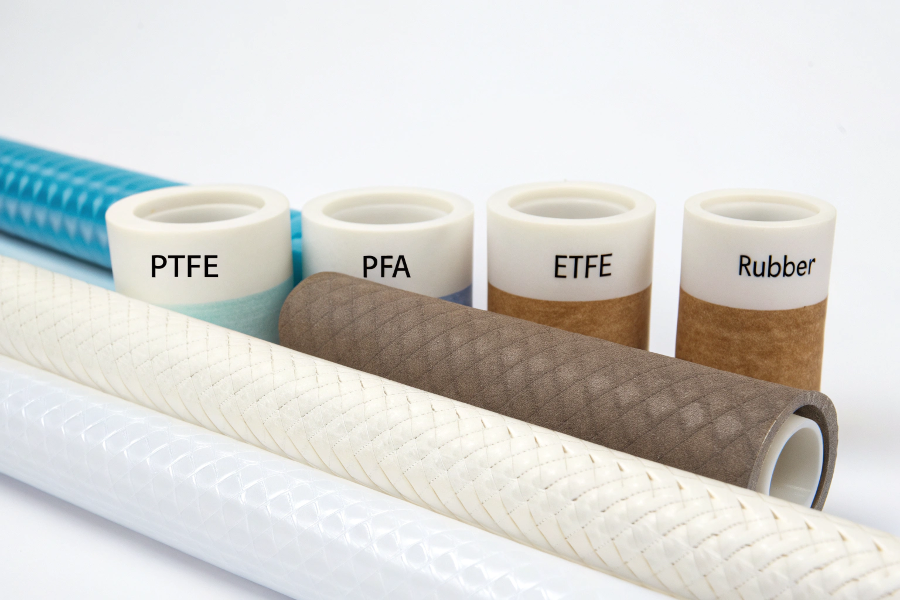

Flow Meter Liner Materials
Based on my installation experience:
Liner Material Selection
Common Materials
Material Temperature Range Best Application PTFE -40°C to 180°C Corrosive fluids Hard Rubber -20°C to 80°C Abrasive slurries PFA -40°C to 200°C High purity Ceramic Up to 800°C Extreme conditions Selection Factors
- Chemical resistance
- Temperature limits
- Wear resistance
- Cost considerations
Application Guidelines
Industry Requirements
- Chemical processing
- Food and beverage
- Water treatment
- Mining operations
Installation Considerations
- Mounting position
- Environmental conditions
- Maintenance access
- Safety requirements
Proper material selection ensures longevity.
How Often Do Flow Meters Need to be Calibrated?
Incorrect calibration intervals can lead to measurement drift and compliance issues.
Flow meters typically require calibration every 6-12 months, though frequency varies based on application, regulatory requirements, and manufacturer specifications.
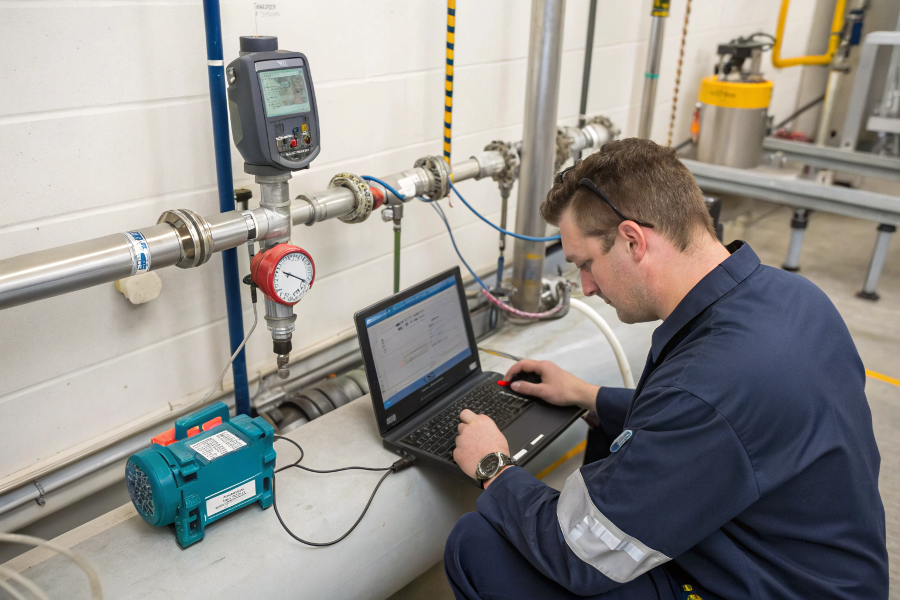

Flow Meter Calibration Process
From my calibration experience:
Calibration Schedule
Industry Standards
Industry Frequency Requirements Custody Transfer 3-6 months High accuracy Process Control 6-12 months Standard accuracy Utilities Annual Compliance focus Non-critical 12-24 months Basic accuracy Influencing Factors
- Process conditions
- Fluid properties
- Accuracy requirements
- Regulatory demands
Calibration Process
Verification Steps
- Zero point check
- Span verification
- Linearity test
- Response time check
Documentation
- Calibration certificates
- Test conditions
- As-found readings
- As-left readings
Regular calibration ensures accuracy.
How Often Should You Clean a Peak Flow Meter?
Dirty flow meters can provide false readings and compromise system efficiency.
Peak flow meters should be cleaned after each use for hygienic applications, while industrial meters typically require cleaning every 3-6 months depending on fluid conditions.
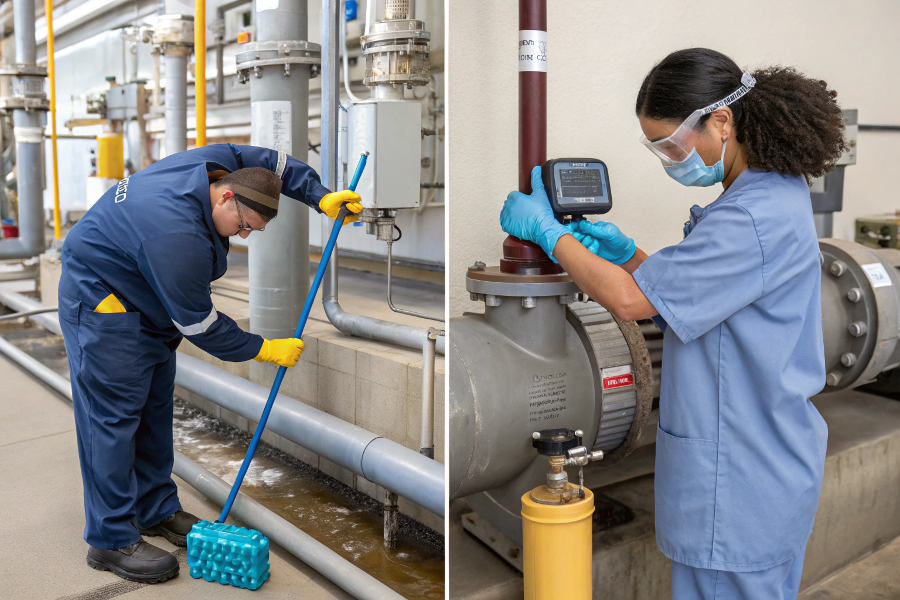

Flow Meter Cleaning Procedures
Based on my maintenance protocols:
Cleaning Requirements
Cleaning Schedule
Application Frequency Method Sanitary After each use CIP/SIP Industrial Quarterly Manual/CIP Utility Semi-annual Basic flush Laboratory Monthly Detailed clean Cleaning Methods
- Chemical cleaning
- Mechanical cleaning
- Ultrasonic cleaning
- Steam sterilization
Maintenance Procedures
Cleaning Steps
- Disassembly (if required)
- Cleaning application
- Inspection
- Reassembly
Quality Checks
- Visual inspection
- Performance testing
- Documentation
- Validation
Regular cleaning ensures performance.
Conclusion
Proper flow meter maintenance, including regular cleaning, calibration, and appropriate material selection, is essential for accurate measurements and extended equipment life.



