Many technicians assume vortex meters work equally well in all orientations – until measurement errors appear. Orientation impacts performance more than expected.
Vortex flow meters can be installed vertically, with liquids requiring upward flow and gases typically needing downward flow. Vertical installation eliminates air bubbles in liquids and prevents liquid accumulation in gas streams, but still demands proper straight-run distances (15D upstream/5D downstream typically).
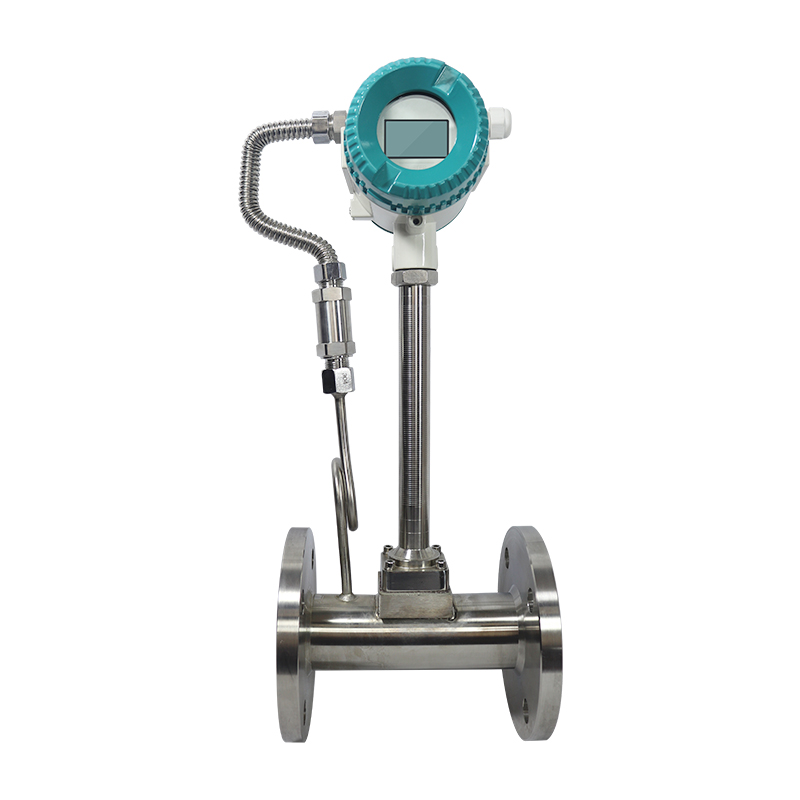

Vortex Flow Meter
The choice between vertical and horizontal installation depends on fluid properties, process conditions, and accuracy requirements.
Can Vortex Flow Meters Be Installed Vertically?
Three key vertical installation scenarios:
Orientation Guidelines Table
| Fluid Type | Preferred Orientation | Reasons | Common Mistakes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liquids | Vertical upward | Prevents air pockets | Installing downward |
| Gases | Vertical downward | Avoids liquid collection | Wrong flow direction |
| Steam | Vertical upward | Ensures condensate drainage | No drip leg |
Installation Advantages
For Liquids:
- Eliminates trapped air
- Reduces sediment buildup
- Improves accuracy >1%
For Gases:
- Prevents liquid pooling
- Better for wet gas streams
- Easier condensate removal
For Steam:
- Automatic water drainage
- Maintains steam quality
- Prevents water hammer

Fluid-Specific Orientation
Special Considerations
- Two-Phase Flow: Generally not recommended
- High Viscosity: May require horizontal
- Slurries: Vertical preferred but check abrasion
- Cryogenic: Vertical upward prevents flashing
- Corrosive: Orientation affects wear patterns
Why Should the Gas Flowmeter Be Installed in Vertical Position?
Four technical reasons for vertical gas installation:
Gas Flow Challenges & Solutions
| Problem | Vertical Solution | Horizontal Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Liquid Accumulation1 | Drains downward | Pooling causes errors |
| Condensate | Falls by gravity | Blockages form |
| Density Changes2 | Consistent flow | Stratification |
| Pulsation | Dampened naturally | Amplified effects |
Installation Best Practices
Downward Flow Configuration
- Meter below process pipe
- Condensate legs optional
- Supports properly aligned
Piping Connections
- Use concentric reducers
- Avoid dead-legs
- Proper gasket selection
Environmental Protection
- Weatherproof enclosures
- Heating when needed
- Vibration isolation

Proper Gas Meter Orientation
Maintenance Benefits
- Easier liquid removal
- Less sensor contamination
- Improved diagnostic access
- Reduced freezing risk
- Clearer visual inspections
What Are the Straight Run Requirements for a Vortex Flowmeter?
Five factors affecting straight-run needs:
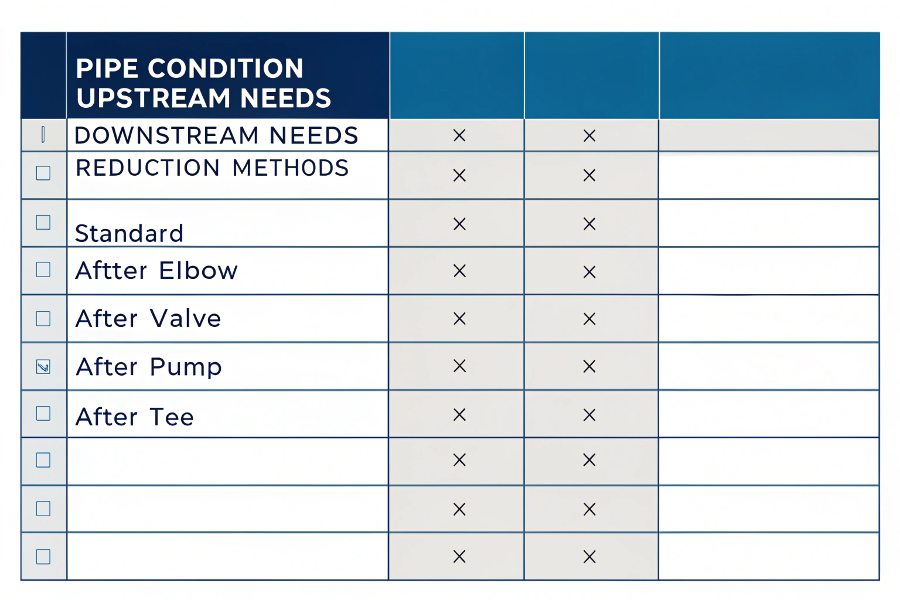
Straight-Run Requirements Table
| Pipe Condition | Upstream Needs | Downstream Needs | Reduction Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | 15D | 5D | None |
| After Elbow | 25D | 5D | Flow conditioner |
| After Valve | 30D | 10D | Double length |
| After Pump | 50D | 15D | Pulsation dampener |
| After Tee | 40D | 10D | Special conditioner |
Measurement Impact Data
- 15D upstream: ±1% accuracy
- 10D upstream: ±2.5% accuracy
- 5D upstream: ±5% or worse
- Proper downstream: Affects K-factor
- Inadequate runs: Causes signal noise
Pipe Configuration Impact
When Space is Limited
Flow Conditioner Options
- Perforated plate (50% reduction)
- Tube bundle (40% reduction)
- Etoile-type (60% reduction)
Alternative Solutions
- Modify pipe layout
- Relocate meter
- Choose different technology
Accuracy Tradeoffs
- Calculate cost of error
- Consider process impact
- Evaluate alternatives
How to Install a Vortex Flow Meter?
Seven-step installation procedure:
Step-by-Step Installation Guide
Site Preparation
- Verify pipe cleanliness
- Check support structures
- Confirm accessibility
Orientation Selection
- Determine fluid type
- Choose proper direction
- Mark flow direction
Straight-Run Verification
- Measure distances
- Identify disturbances
- Install conditioners if needed
Mechanical Installation
- Proper gasket alignment
- Torque bolts evenly
- Check for leaks
Electrical Connections
- Correct wiring
- Proper grounding
- Conduit sealing
Pre-Startup Checks
- Sensor verification
- Zero calibration
- Signal testing
Commissioning
- Gradual process start
- Initial readings
- Performance logging

Installation Process Flow
Installation Tools Checklist
- Pipe cutters/deburring tool
- Alignment lasers
- Torque wrench
- Multimeter
- Pressure gauge
- Leak detection equipment
- Calibration certificate
Conclusion
Vortex flow meters work well vertically when properly oriented (upward for liquids/downward for gases) and maintain standard straight-run requirements (15D/5D). Vertical installation solves specific flow problems but requires careful planning regarding fluid properties, piping configuration, and maintenance access. Following systematic installation procedures ensures optimal meter performance regardless of orientation while allowing for space constraints through proper alternatives when needed.



