Measuring flow in small pipes demands precision traditional methods can’t deliver. Ultrasonic technology rises to this challenge with groundbreaking accuracy.
Ultrasonic flow meters achieve ±0.5-1% accuracy in narrow pipes by measuring the time difference between upstream/downstream ultrasonic signals, outperforming mechanical meters which typically offer only ±2-5% accuracy in small diameters due to frictional losses and installation effects.
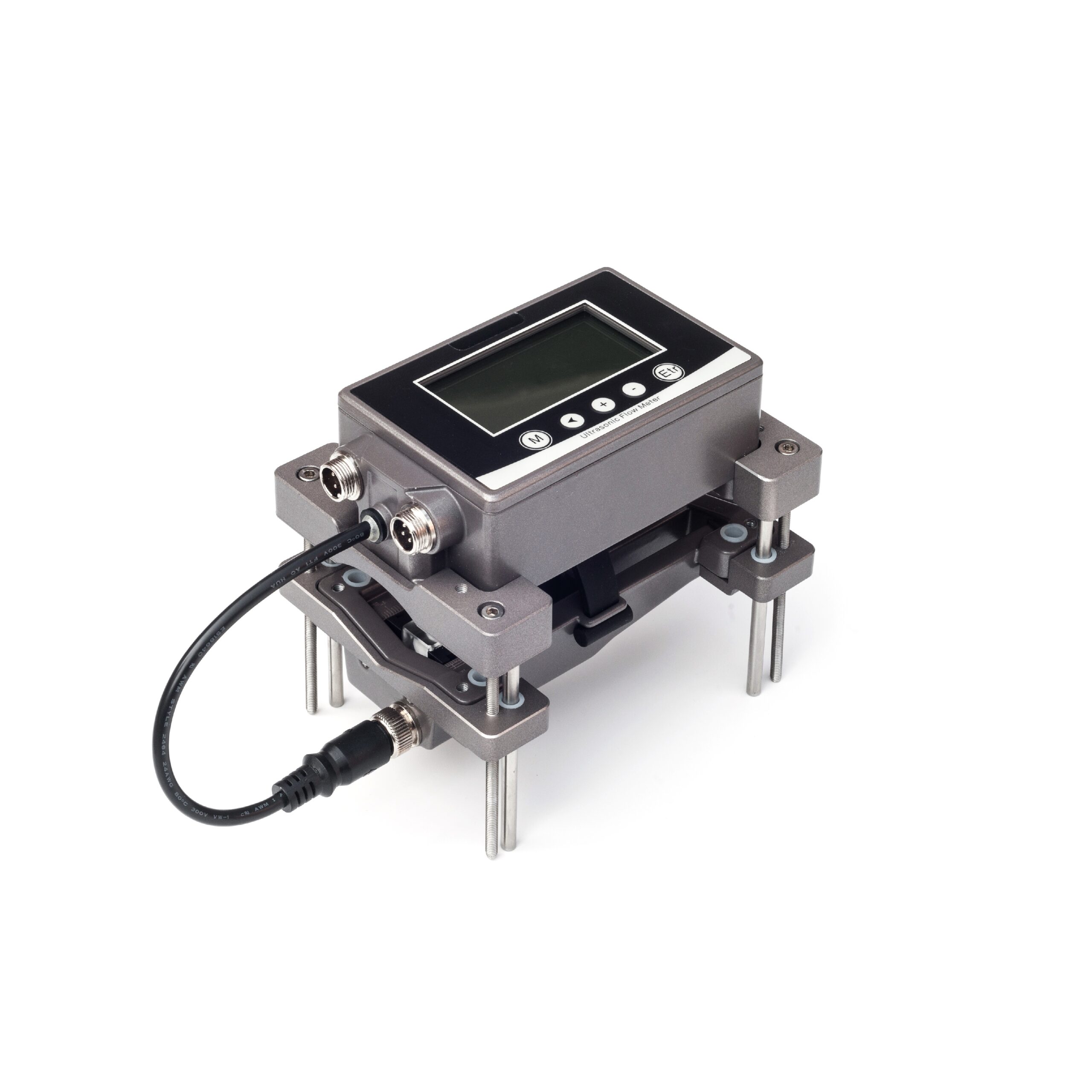

Ultrasonic Flow Meter in Small Pipes
The unique capabilities of ultrasonic measurement transform small pipe monitoring. Let’s explore these advantages in depth.
What Is the Accuracy of an Ultrasonic Flow Meter?
Precision levels vary by installation conditions:
Typical Accuracy Ranges
| Pipe Size | Installation Type | Best Accuracy | Typical Accuracy | Worst Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DN10-DN25 | Inline wetted | ±0.5% rate | ±1% | ±3% |
| DN25-DN50 | Clamp-on | ±1% | ±1.5% | ±5% |
| <DN10 | Special micro | ±2% | ±3% | ±10% |
Accuracy by Pipe Size
Factors Affecting Accuracy in Small Pipes
- Transducer alignment – 0.5° misalignment causes >1% error
- Flow profile distortion – Needs 10D straight pipe runs
- Fluid turbidity – Particles >50μm degrade signal
- Pipe wall thickness – Affects ultrasonic transmission
- Temperature gradients – Changes sound velocity
Improving Measurement Precision
- Multi-beam measurement paths
- Automatic signal quality adjustment
- Predictive error compensation
- Regular zero-flow calibration
- Advanced DSP filtering
What Is the Most Accurate Type of Flowmeter?
Competitive technologies in small pipes:
Accuracy Comparison Table
| Technology | Small Pipe Accuracy | Best Pipe Size | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coriolis mass | ±0.1% | DN4-DN40 | High pressure drop |
| Ultrasonic | ±0.5% | DN6-DN50 | Requires clean fluid |
| Positive displacement | ±0.5% | DN8-DN25 | Moving parts wear |
| Turbine | ±1% | DN10-DN50 | Bearing failure risk |
| Differential pressure | ±2% | DN15-DN50 | Limited turndown ratio |
Situational Superiority
- Highest absolute accuracy – Laboratory-grade Coriolis
- Best balance – Multi-beam ultrasonic
- Viscous fluids – Positive displacement
- Transient flows – Fast-response turbine
- Low maintenance – Clamp-on ultrasonic
Emerging Accuracy Leaders
- Hybrid ultrasonic/Coriolis designs
- Micro-electrical impedance meters
- MEMS-based flow sensors
- AI-compensated ultrasonic models
- Quantum measurement prototypes
What Are the Disadvantages of Ultrasonic Flowmeter?
Challenges in compact installations:
Critical Limitations in Small Pipes
- Minimum flow velocity – Typically 0.3m/s (versus 0.1m/s for Coriolis)
- Gas bubble sensitivity – >0.5% gas content causes errors
- Pipe material restrictions – Limited to metals/plastics
- Installation strictness – Needs perfect transducer alignment
- Power requirements – Consumes 5-10W continuously
Small-Pipe Specific Challenges
| Issue | Impact (1-10) | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Signal attenuation | 8 | High-frequency transducers |
| Vibration effects | 7 | Isolation mounting |
| Wall thickness | 6 | Thickness compensation |
| Laminar flow | 5 | Flow conditioners |
| Surface roughness | 4 | Internal polishing |

Small-Pipe Challenges
When Not to Choose Ultrasonic
- Heavy slurries with >10% solids
- Non-conductive pure organics
- Pipes with thick insulation
- Highly pulsating flows
- Applications needing <0.3m/s measurement
How Accurate Is a Flow Meter Reading?
Understanding real-world performance:
Measurement Uncertainty Components
- Basic meter accuracy – Typically ±0.5-1%
- Installation effects – Adds 0.5-2%
- Process conditions – Contributes 0.3-3%
- Fluid properties – Accounts for 0.2-5%
- Calibration drift – Usually <0.5%/year
Total Uncertainty Calculation
| Component | Weight % | Small Pipe Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Instrument | 50% | Major |
| Installation | 30% | Critical |
| Process | 15% | Moderate |
| Fluid | 5% | Minor |

Accuracy Breakdown
Optimizing Real-World Accuracy
- Factory wet calibration
- Annual verification checks
- Continuous signal monitoring
- Automated compensation
- Redundant measurement paths
- Advanced diagnostics
Conclusion
Ultrasonic flow meters deliver unmatched accuracy (±0.5-1%) in small pipes through non-intrusive measurement, outperforming mechanical alternatives despite installation sensitivity. While requiring careful setup and facing fluid limitations, their precision, low maintenance, and versatility make them ideal for critical narrow pipe applications when properly implemented. Continuous improvements in transducer technology and signal processing push the boundaries of small-pipe flow measurement accuracy.



