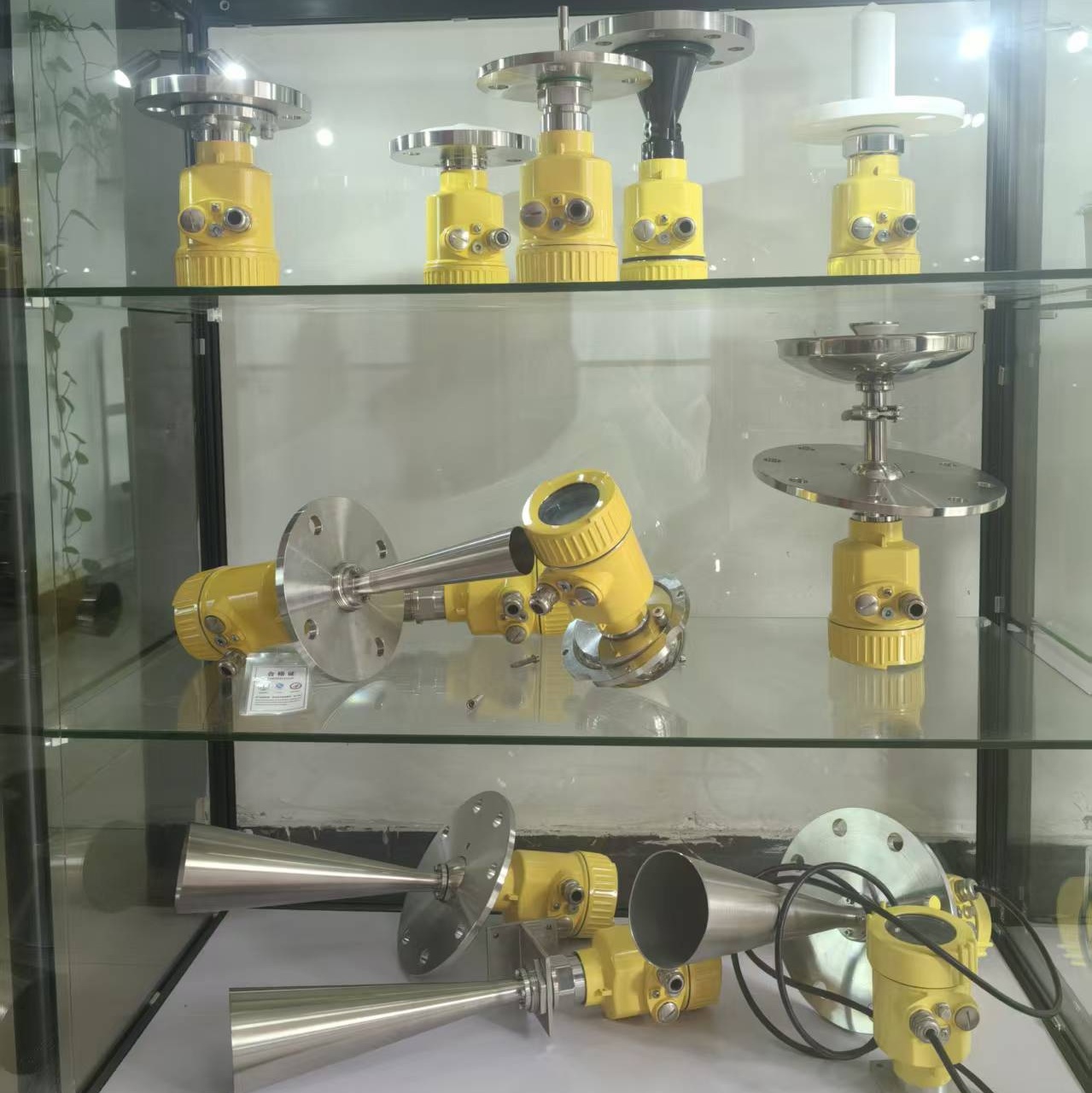
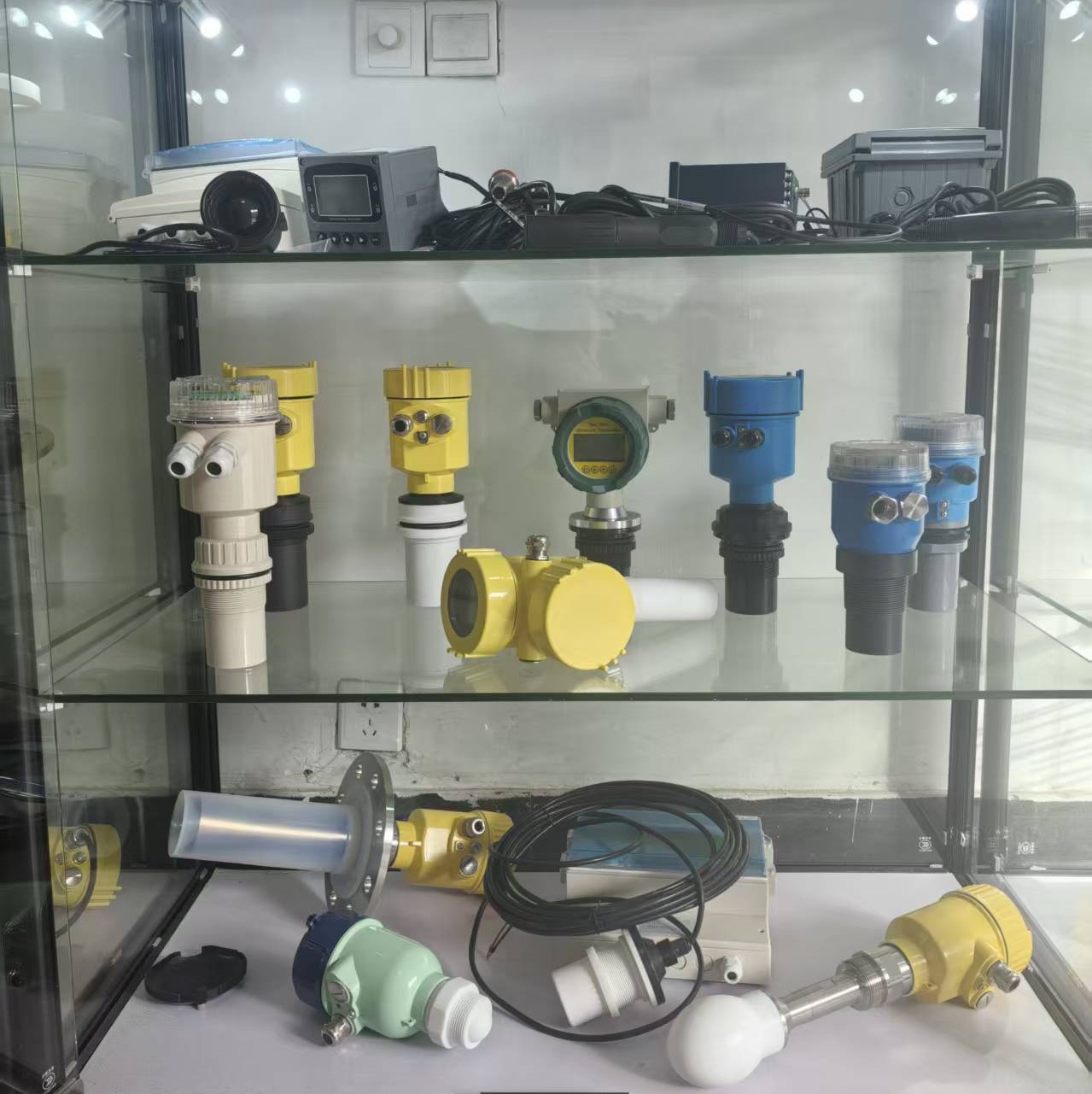
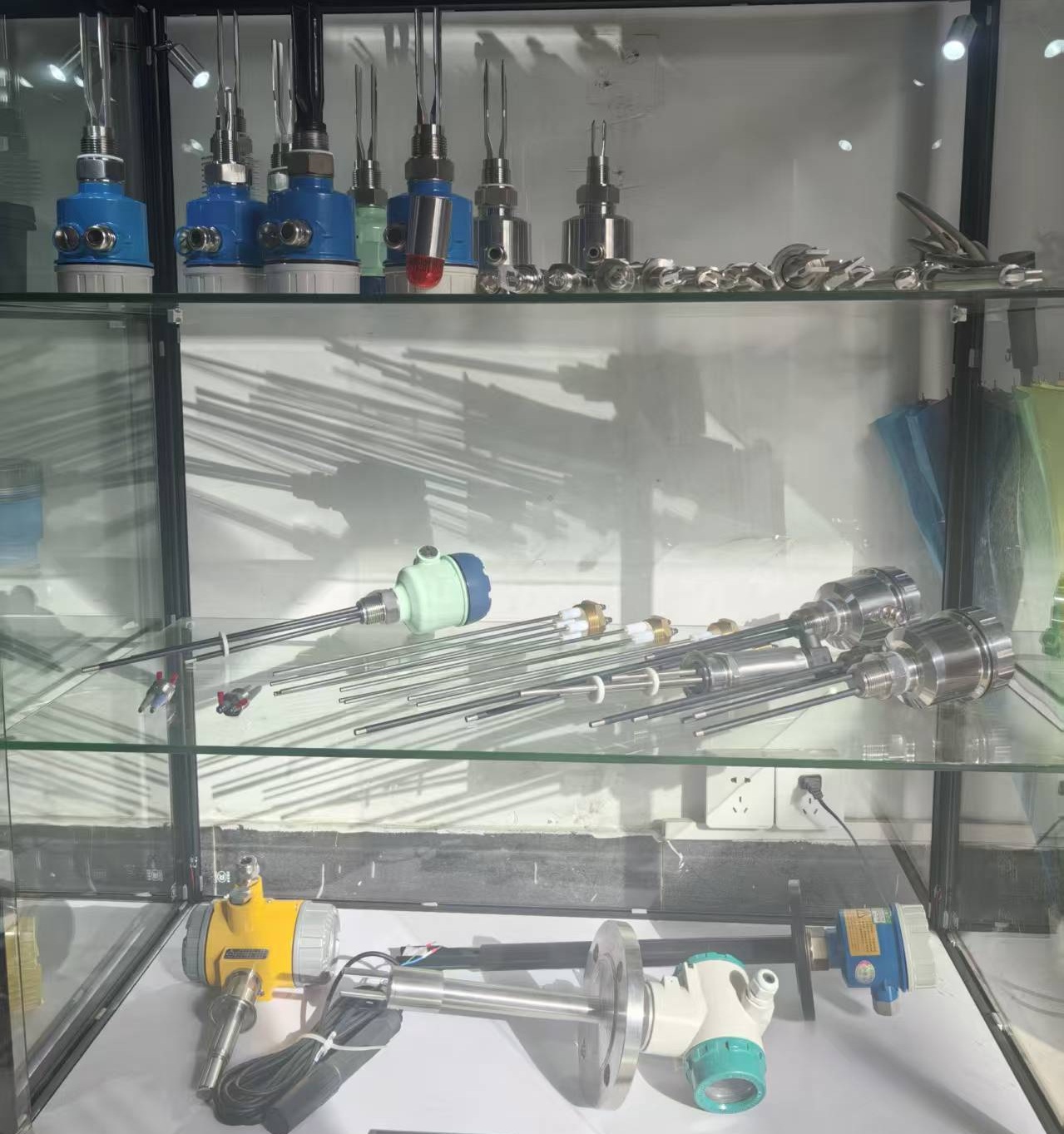
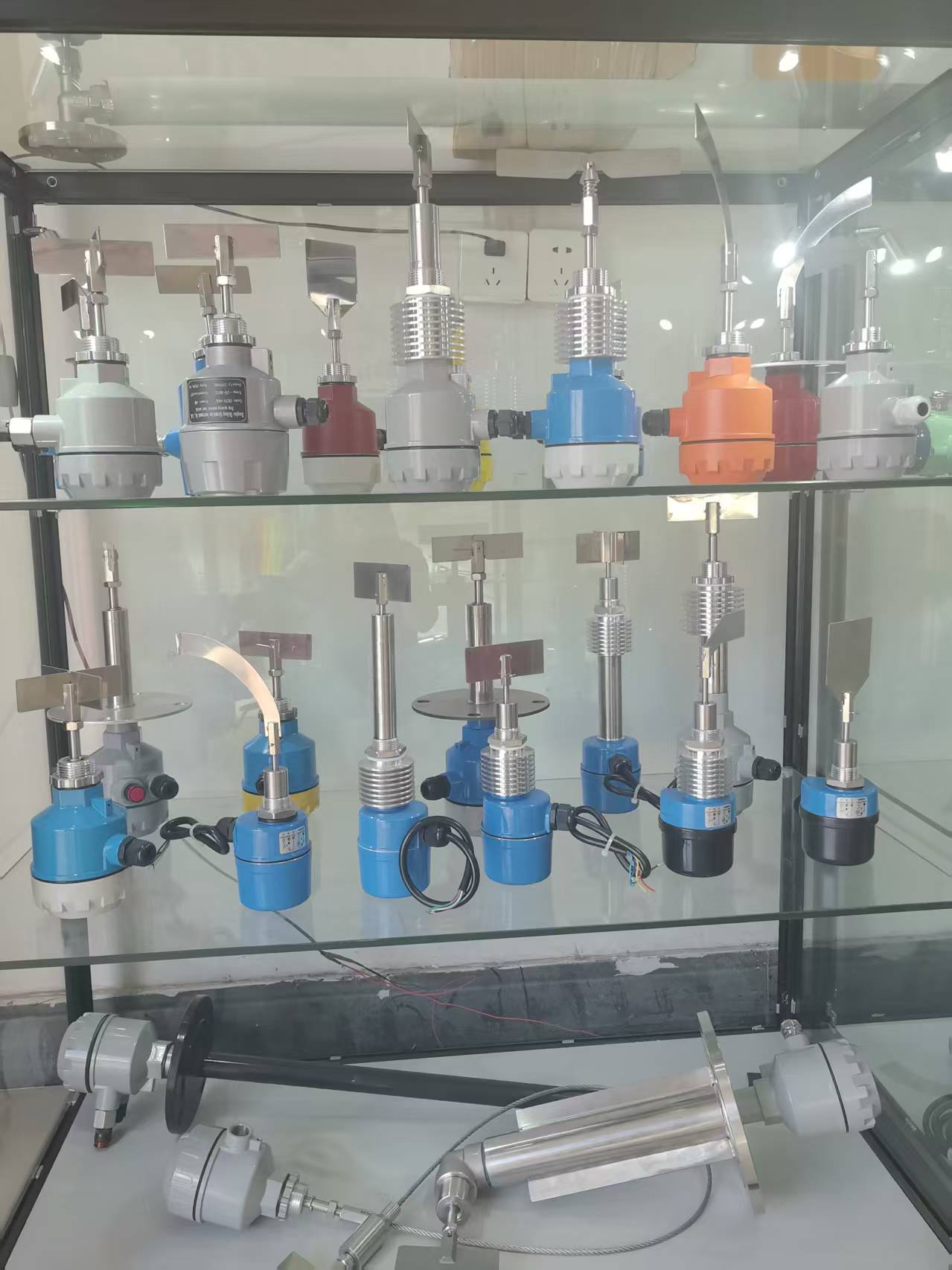
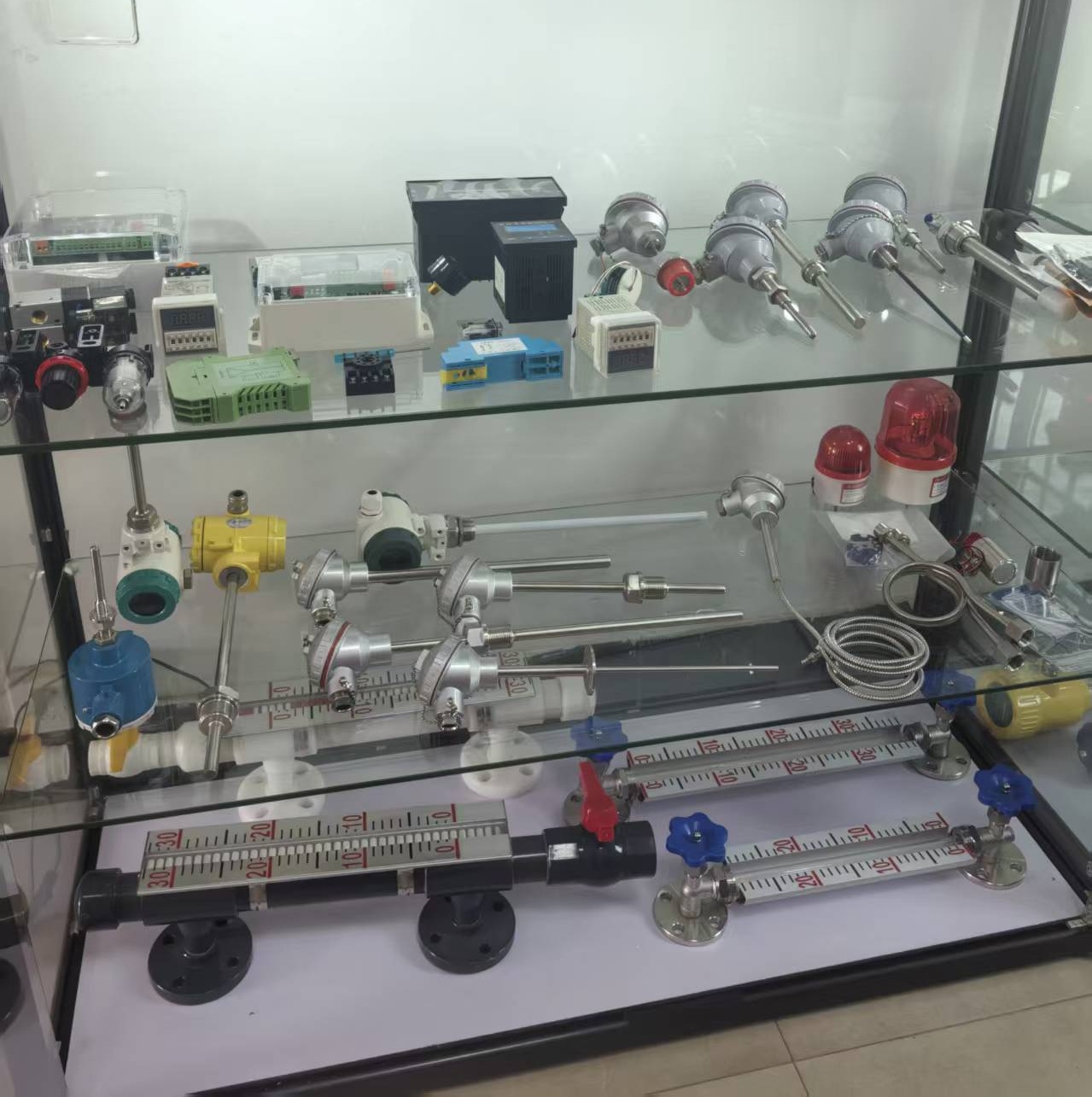
Radar level meter
A Radar Level Meter is a non-contact device that uses electromagnetic waves to measure liquid or solid levels in tanks or vessels. It emits high-frequency radar signals that reflect off the material surface and calculates the level based on the time delay of the return signal. Suitable for various industries, it offers high accuracy, operates in extreme conditions (temperature, pressure), and handles challenging media like foam or vapors. Ideal for liquids, powders, and bulk solids, it ensures reliable, maintenance-free performance.
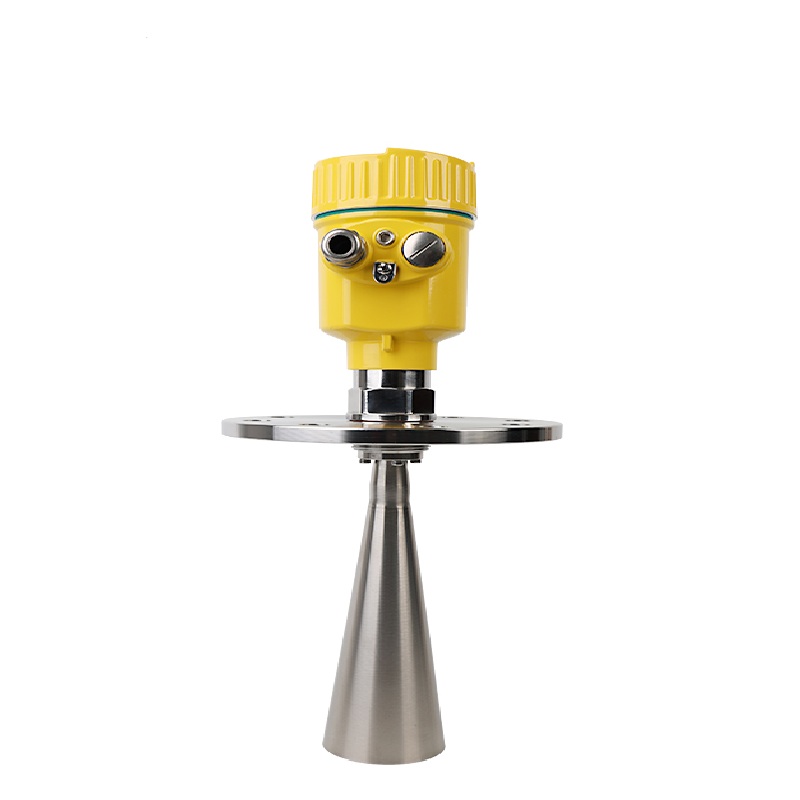

26G radar level meter for solid
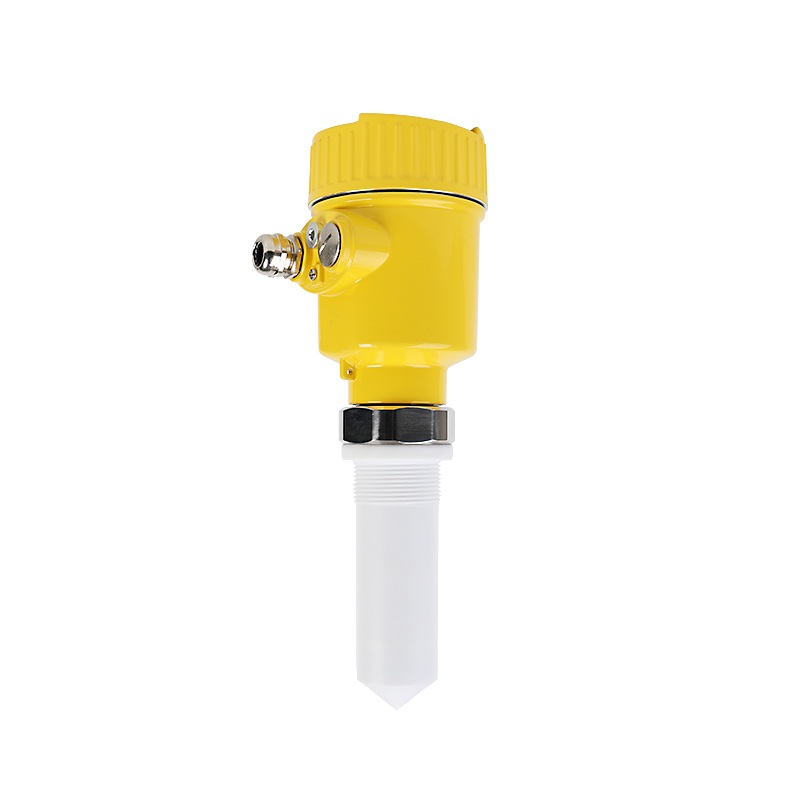

26G radar level meter
for corrosive liquid
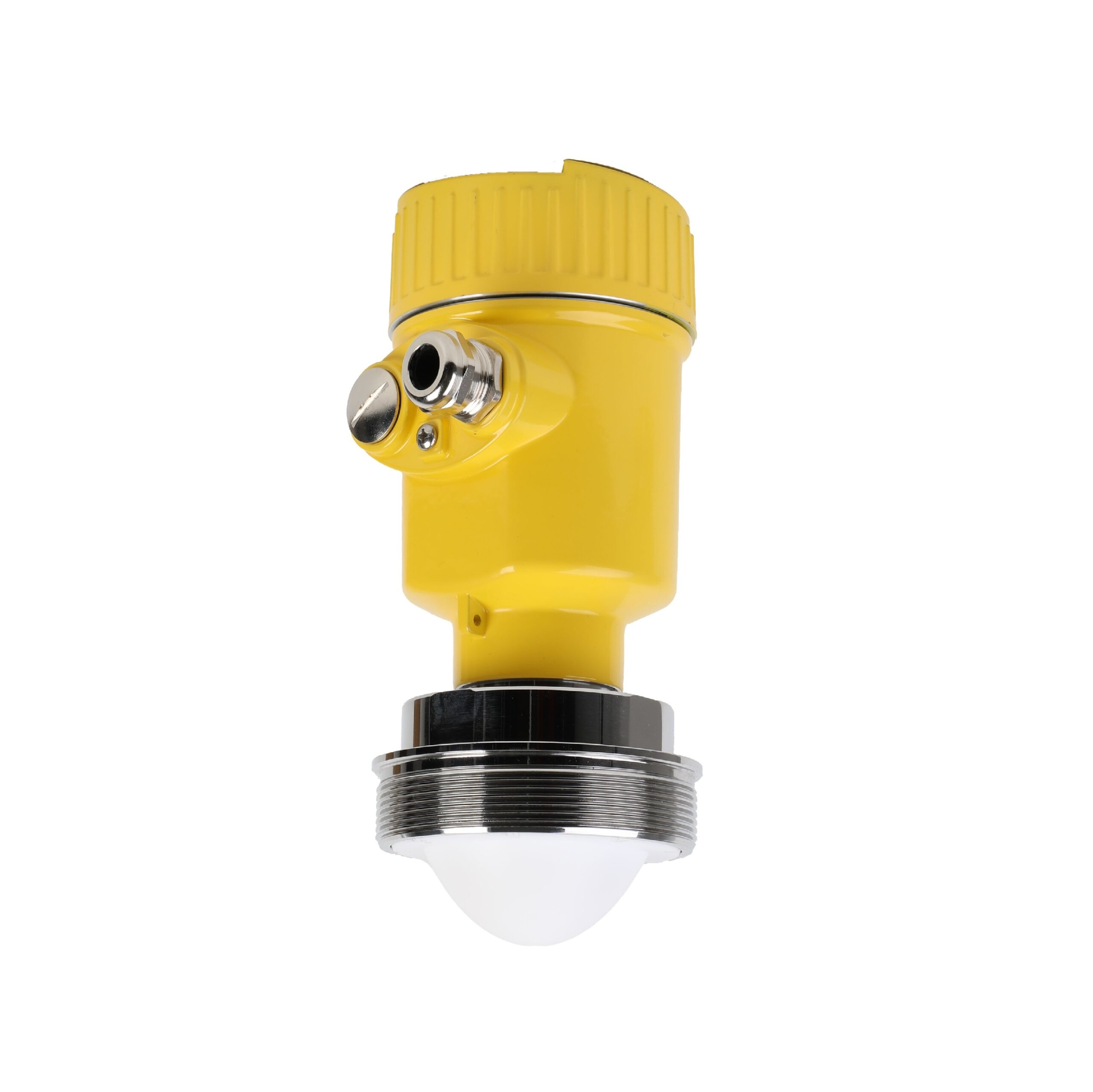

80G radar level meter
for solid or liquid
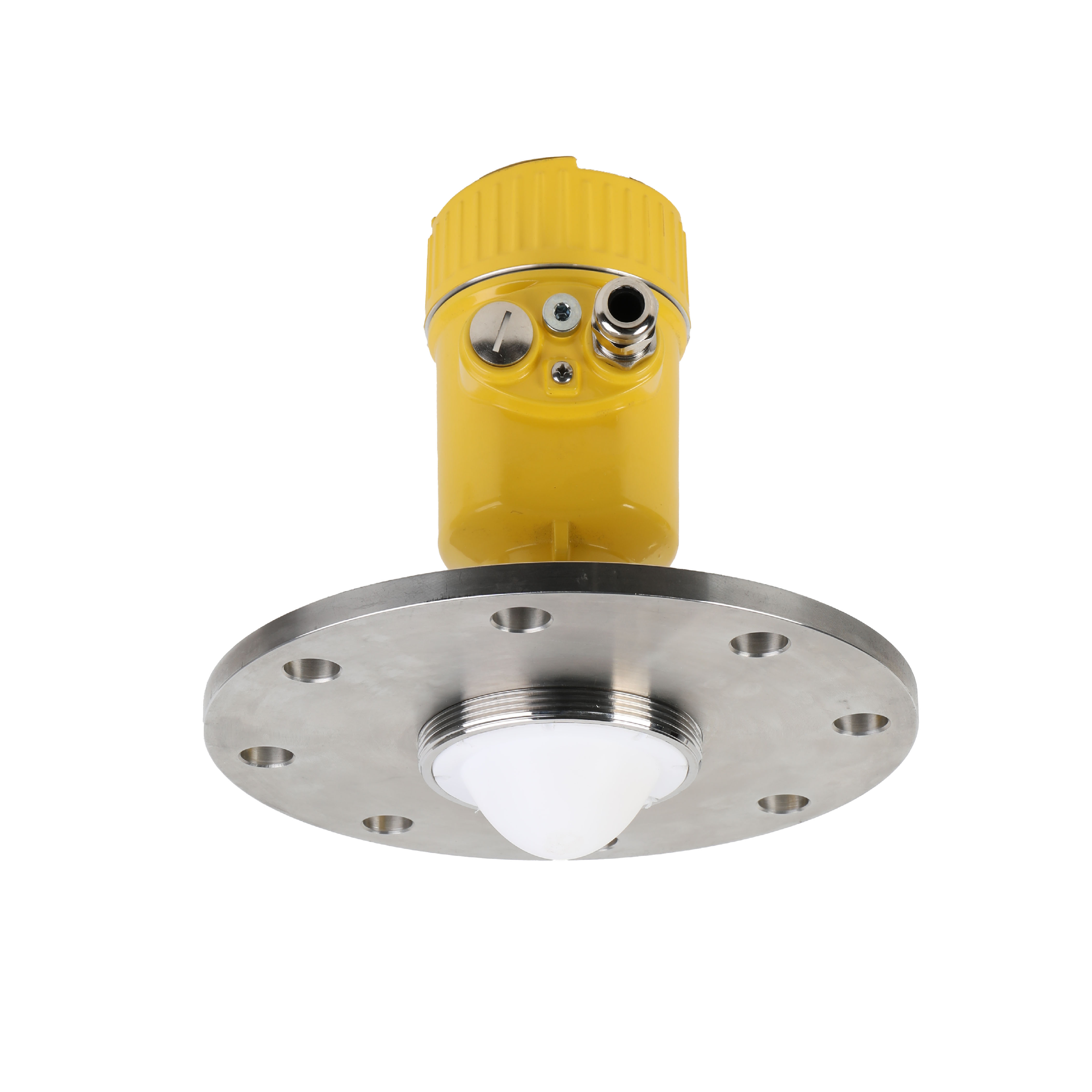

80G radar level meter
for solid
All You Need to know About radar level Meter
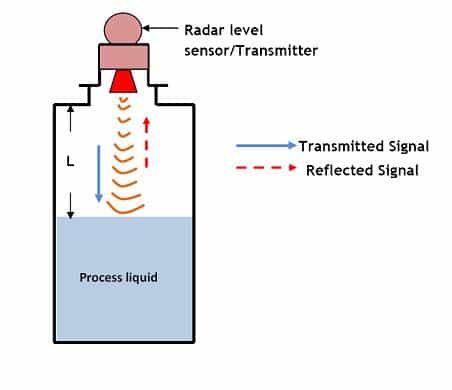
radar level meter principle
The principle of a Radar Level Meter is based on Time of Flight (ToF) technology. It emits high-frequency electromagnetic waves (typically microwaves) toward the material surface. These waves reflect off the surface and return to the sensor. The device calculates the distance to the material by measuring the time delay between the transmitted and reflected signals. This distance is then converted into a level measurement. The non-contact method ensures accuracy and reliability, even in challenging conditions like foam, vapors, or extreme temperatures.
Advantages of radar level meter
Non-contact measurement
No wear and tear.
Unaffected by foam, dust, or vapor
Reliable in challenging environments.
Versatile
Works with liquids, solids, powders, and slurries.
Wide Application
Ideal for industries like chemical, oil & gas, and food & beverage.
radar level meter application
Oil & Gas Industry
Chemical Industry
Water & Wastewater Treatment
Power Generation
Food & Beverage Industry
Pharmaceutical Industry
Mining & Minerals
Pulp & Paper Industry
Agriculture
Marine Industry

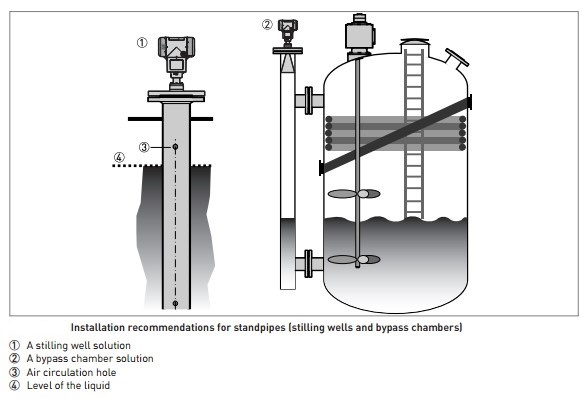
Installation Requirement
- Ensure a clear signal path; avoid obstructions like agitators or ladders.
- Install perpendicular to the liquid or solid surface.
- Use suitable mounting flanges for tank compatibility.
- Maintain proper distance from walls or internal structures.
- Verify compatibility with process conditions (temperature, pressure).
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for power supply and grounding.
Production Process








