Frustrated by inaccurate flow measurements in your narrow pipelines? Compact ultrasonic flow meters solve unique small-pipe challenges traditional meters can’t handle. Even 0.1mm alignment errors cause significant reading errors in DN15 pipes.
Ultrasonic flow meters measure fluid velocity by analyzing ultrasonic wave transit times, ideal for small pipes (DN8-DN50) where conventional meters fail. They offer non-intrusive, bi-directional measurement with ±0.5-1% accuracy when properly installed, though bubble presence and pipe material affect performance. Modern designs overcome traditional small-pipe limitations.
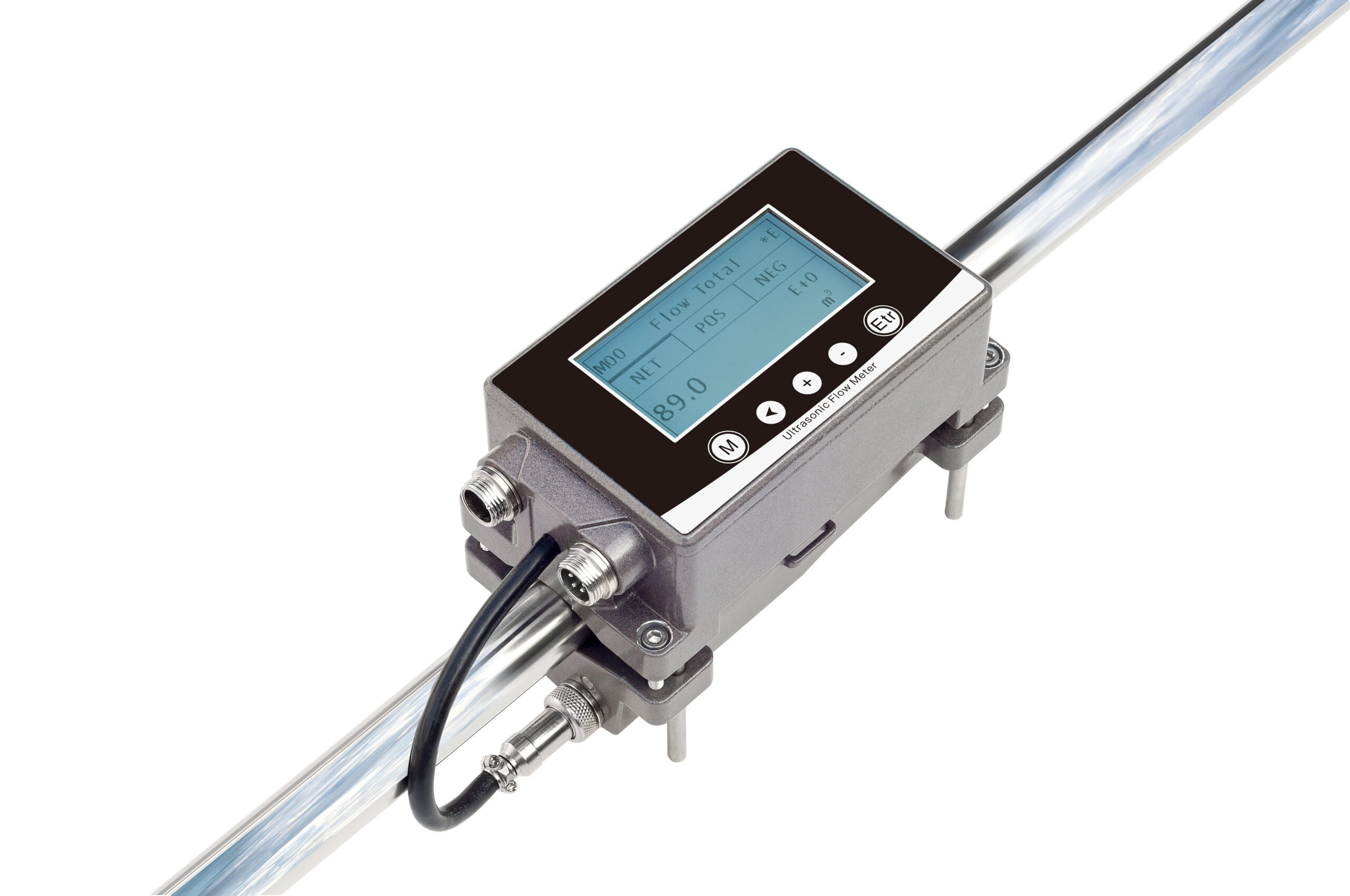

Ultrasonic Flow Meter for Small Pipes
Understanding ultrasonic flow meter fundamentals helps optimize their use in confined spaces. Let’s examine key operational aspects.
What Is the Purpose of the Ultrasonic Flow Meter?
Core functions in compact pipelines:
Primary Applications in Small Pipes
| Application | Pipe Size Range | Special Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical dosing | DN8-DN15 | Chemical-resistant wetted parts |
| Lab research | DN6-DN10 | High-frequency transducers (5MHz) |
| Medical gas systems | DN10-DN20 | Sanitary design certification |
| Semiconductor cooling | DN15-DN25 | Ultra-pure materials |
Unique Small-Pipe Advantages
- No pressure drop – Critical in low-flow systems
- Bi-directional measurement – Essential for loop systems
- Wide turndown ratio – Handles fluctuating flows
- Multi-variable output – Simultaneous flow/temperature data

Typical Installation Scenarios
Emerging Niche Uses
- Microbrewery ingredient control
- Pharmaceutical precursor mixing
- HVAC refrigerant monitoring
- Fuel cell reactant management
What Are the Disadvantages of an Ultrasonic Flow Meter?
Key limitations in confined installations:
Small-Pipe Specific Challenges
| Issue | Impact Below DN25 | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Signal attenuation | 3x worse than DN50 | Use higher frequency (2-5MHz) |
| Beam alignment | 0.1° error = 2% error | Precision machined spool pieces |
| Reflection interference | More pronounced | Anti-reflective coatings |
| Temperature effects | Expansion more critical | Integrated temperature sensors |
General Limitations
- Bubble sensitivity – Fails above 5% gas content
- Pipe material constraints – Doesn’t work well with lined pipes
- Installation precision – Requires trained technicians
- Upfront cost – 2-3x traditional meter price

Technical Constraints Visualized
When Not to Use Ultrasonic
- Slurry flows >5% solids
- Non-conductive liquids (pure oils)
- Unstable flow profiles
- Highly aerated liquids
How Accurate Is an Ultrasonic Flow Meter?
Performance metrics by pipe size:
Typical Accuracy Ranges
| Condition | Small Pipe (DN8-DN25) | Standard Pipe (DN25+) |
|---|---|---|
| Ideal installation | ±0.5% of reading | ±0.3% of reading |
| Challenging conditions | ±1.5% of reading | ±0.8% of reading |
| Uncompensated temp | Additional ±0.1%/°C | Additional ±0.05%/°C |
Accuracy Factors in Small Pipes
- Transducer frequency – Higher = better resolution
- Number of paths – Single vs. multi-path
- Signal processing – Advanced algorithms help
- Calibration method – Wet calibration preferred
Performance Benchmarking
Improving Accuracy
- Regular zero checks
- Proper pipe coupling
- Stable temperature maintenance
- Adequate straight runs
- Professional installation
What Are the Two Types of Ultrasonic Flow Meters?
Technology comparison for small pipes:
Transit-Time vs. Doppler
| Parameter | Transit-Time | Doppler |
|---|---|---|
| Working principle | Measures time difference | Detects frequency shift |
| Small pipe suitability | Excellent (DN8+) | Poor (<DN50 ineffective) |
| Fluid requirements | Clean, bubble-free | Contains particles/bubbles |
| Typical accuracy | ±0.5-1% | ±2-5% |
| Price range | $$$$ | $$ |
Transit-Time Subtypes
- Inline wetted – Direct contact, highest accuracy
- Clamp-on – Non-invasive, easier installation
- Insertion – Compromise solution
- Hybrid – Combined technologies
Type Differentiation
Selection Criteria for Small Pipes
- Fluid purity – Dictates transit-time vs Doppler
- Pipe access – Determines clamp-on vs inline
- Budget – Affects technology level
- Future needs – Scalability considerations
Overcoming Small-Pipe Measurement Challenges
Practical Solutions
- Specialized transducers – Higher frequency, focused beams
- Precision adapters – Ensure perfect alignment
- Enhanced algorithms – Compensate for boundary effects
- Multi-path designs – Even in small diameters
Installation Checklist for DN8-DN25
- Verify pipe inner diameter precisely
- Ensure adequate straight runs
- Use proper coupling medium
- Confirm transducer alignment
- Implement temperature compensation
Conclusion
Ultrasonic flow meters provide precise, non-invasive measurement in small pipes (DN8-DN25) when properly selected and installed. While transit-time models achieve ±0.5-1% accuracy in clean fluids, they require careful installation to overcome inherent small-pipe challenges. For critical small-diameter applications in pharmaceuticals, chemicals, or research, invested ultrasonic solutions outperform traditional flow technologies in both accuracy and maintenance requirements. Always match the meter type (transit-time vs Doppler) to your fluid characteristics and consider professional installation assistance for optimal performance in confined pipe sizes.



