Improper level switch connections can lead to equipment damage, process failures, and even dangerous safety situations.
A level switch connection involves proper wiring, mounting, and integration into the control system, typically requiring power supply and signal connections based on the switch type.
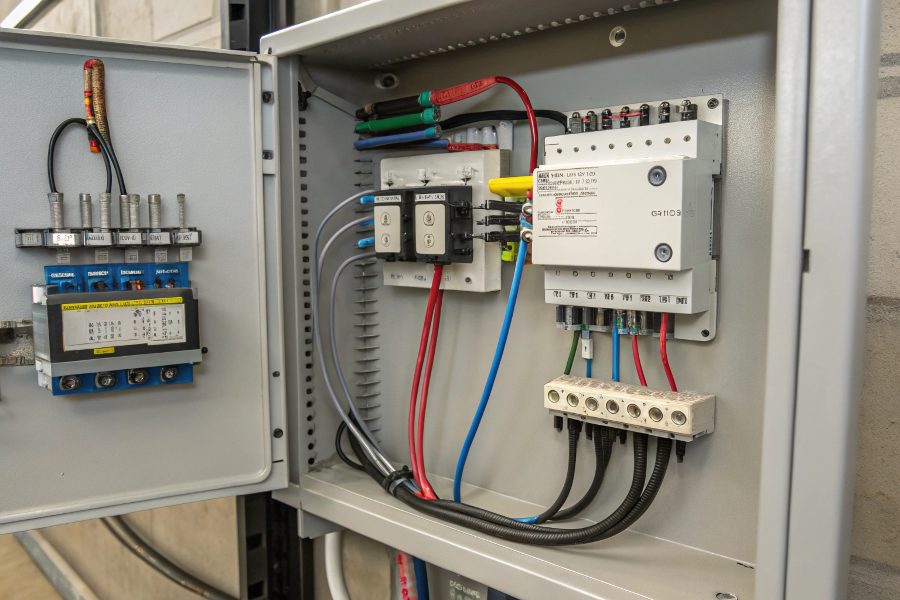

Level Switch Connection Overview
Let me share insights from my years of experience installing and troubleshooting level switches.
How Does a Level Switch Work?
Many users face challenges understanding level switch operation, leading to installation mistakes.
A level switch detects liquid or solid material presence using various technologies (float, vibrating fork, capacitive, etc.), converting physical level detection into an electrical signal.
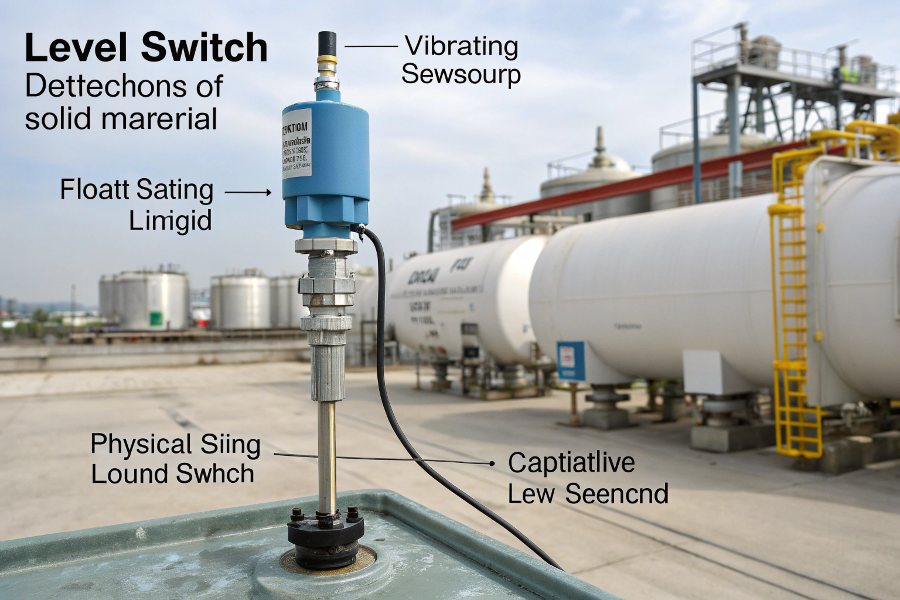
Level Switch Operating Principles
From my field experience:
Operating Principles
Common Technologies
Type Working Principle Signal Output Float Buoyancy Mechanical/Reed Vibrating Frequency change Electronic Capacitive Dielectric change Electronic Optical Light reflection Electronic Detection Methods
- Direct contact
- Non-contact sensing
- Interface detection
- Point level monitoring
Signal Processing
Output Types
- Mechanical contacts
- Electronic switches
- Relay outputs
- Digital signals
Response Characteristics
- Switching delay
- Hysteresis
- Contact ratings
- Fail-safe modes
These principles ensure reliable operation.
How Should a Float Switch Be Wired?
Incorrect float switch wiring can cause false alarms or fail to protect equipment.
Float switches should be wired according to their contact configuration (NO/NC), power requirements, and control system interface, with proper consideration for voltage and current ratings.
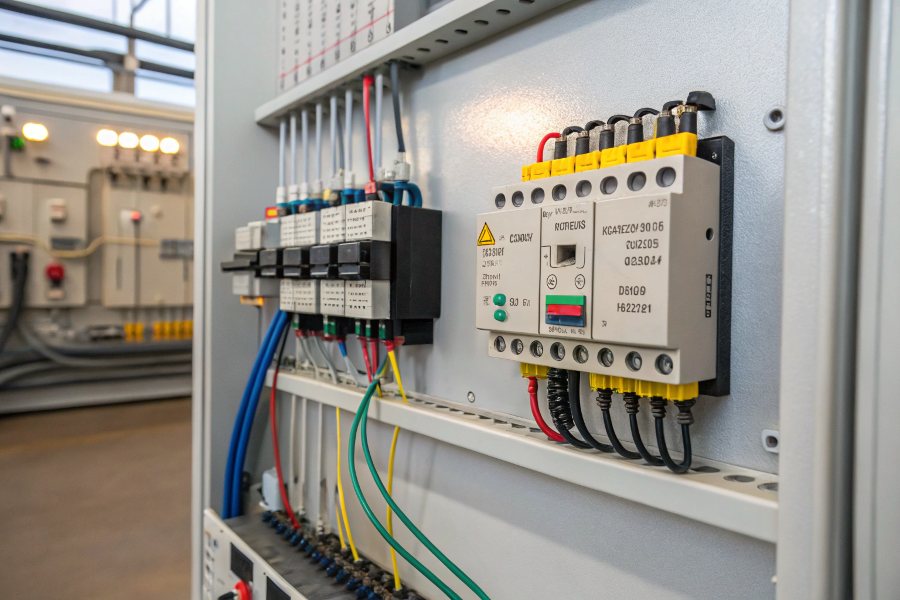
Float Switch Wiring Diagram
Based on my installation experience:
Wiring Guidelines
Connection Types
Configuration Application Circuit Type NO (Normally Open) High level alarm Close on rise NC (Normally Closed) Low level alarm Open on fall SPDT Dual function Changeover Multi-point Multiple levels Multiple switches Installation Requirements
- Cable selection
- Conduit protection
- Seal requirements
- Grounding needs
Safety Considerations
Protection Methods
- Voltage isolation
- Current limitation
- Spark protection
- Environmental sealing
Testing Procedures
- Continuity check
- Insulation test
- Function verification
- Documentation
These guidelines ensure safe installation.
What is the Difference Between a Level Transmitter and a Level Switch?
Understanding this difference is crucial for proper application and connection methods.
Level switches provide binary (on/off) signals at specific points, while transmitters output continuous level measurements, typically as 4-20mA or digital signals.
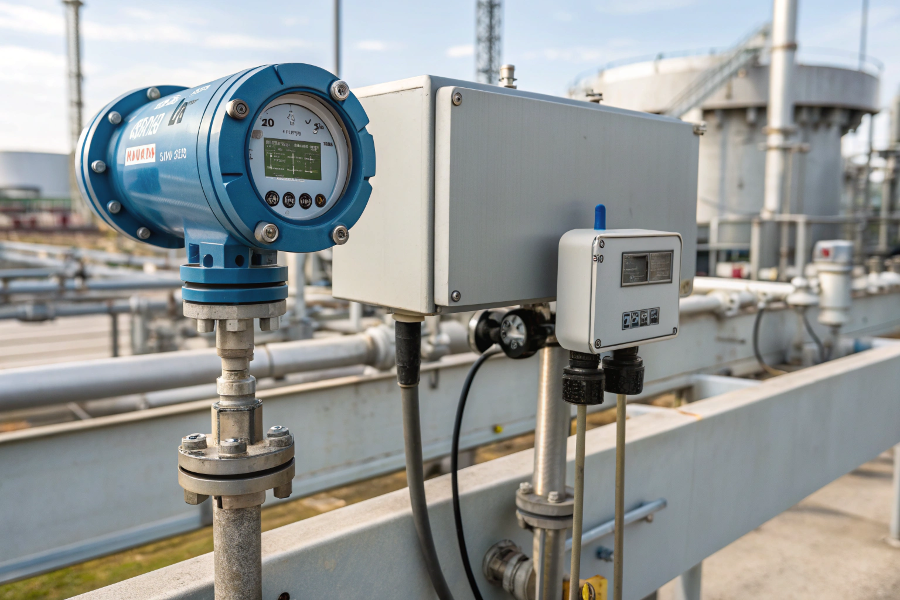

Transmitter vs Switch Comparison
From my system integration experience:
Key Differences
Connection Requirements
Feature Switch Transmitter Power Simple DC/None Loop/External Wiring 2-3 wires 2-4 wires Signal Binary Analog/Digital Interface Direct/PLC PLC/DCS Application Considerations
- Installation complexity
- Maintenance needs
- Cost factors
- System integration
Selection Criteria
Process Requirements
- Control needs
- Safety functions
- Monitoring requirements
- Cost constraints
Integration Aspects
- Control system compatibility
- Power availability
- Signal processing
- Maintenance access
These factors guide proper selection.
What is the Switch Connection?
Many technicians struggle with proper switch connection methods and standards.
Switch connection refers to the electrical interface between the level switch and control system, including power supply, signal wiring, and grounding arrangements.
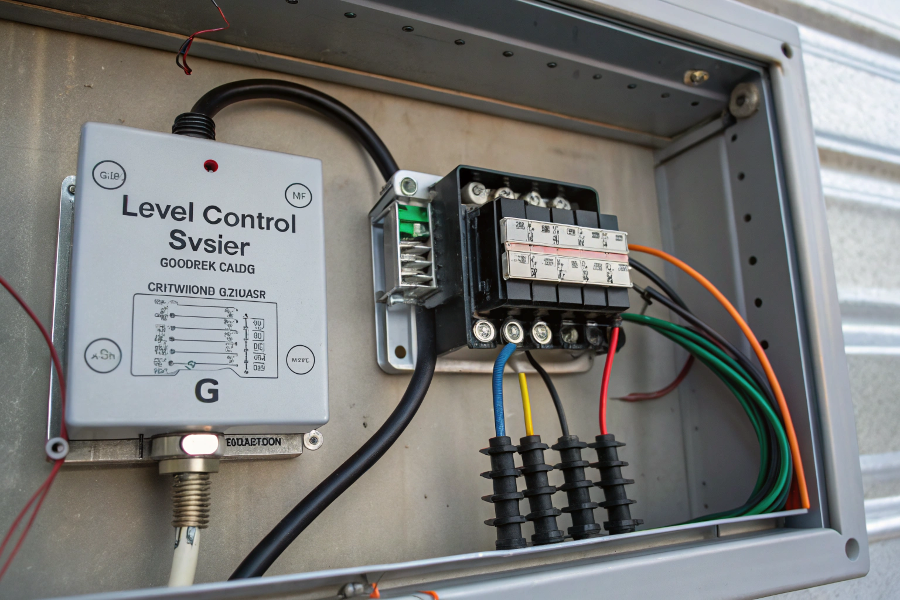

Switch Connection Methods
Drawing from my wiring expertise:
Connection Types
Electrical Configurations
Type Description Application 2-wire Simple contact Basic switching 3-wire Power + signal Electronic switch 4-wire Separate power Complex function Relay Isolated contact Power switching Terminal Arrangements
- Screw terminals
- Quick connect
- Cable glands
- Plug connectors
Installation Requirements
Wiring Standards
- Voltage ratings
- Current capacity
- Cable specifications
- Protection class
Safety Measures
- Isolation barriers
- Surge protection
- Hazardous area
- Environmental protection
These specifications ensure proper installation.
Conclusion
Proper level switch connection requires understanding of switch types, wiring methods, and safety requirements to ensure reliable operation and system protection.



