Getting the most out of your insertion flow meter starts with proper installation. A correctly installed meter can maintain ±2-5% accuracy in most applications.
To install an insertion flow meter: 1) Choose the optimal pipe location, 2) Drill and mount the hot tap fitting, 3) Insert the probe to the specified depth, 4) Align properly to flow direction, and 5) Secure connections while allowing for thermal expansion – following these steps ensures accurate flow measurements from day one.
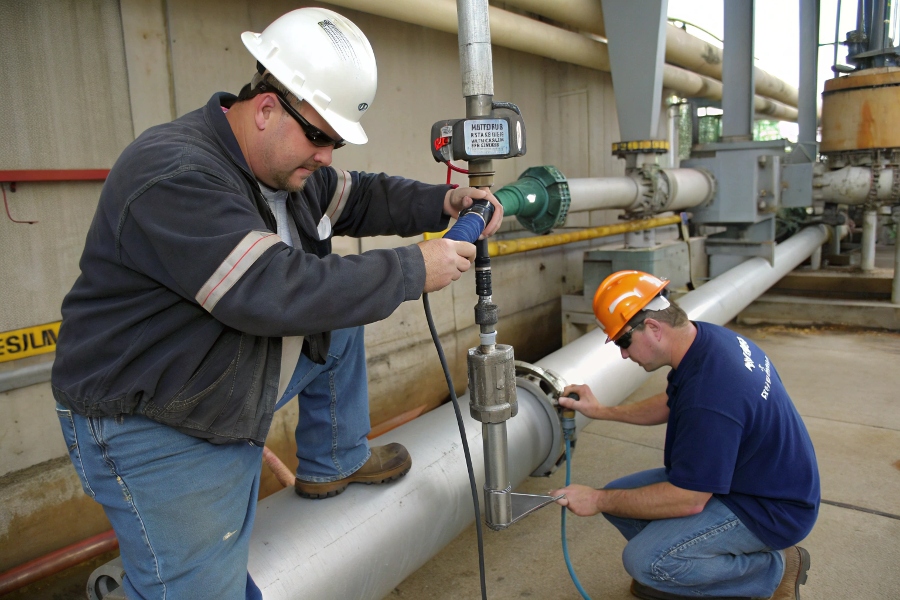

Proper Insertion Flow Meter Installation
With hundreds of successful installations under our belt, we can confidently share these professional techniques.
What Is an Insertion Type Flow Meter?
Understanding your measurement device is the first step.
An insertion flow meter is a type of flow measurement device where only a probe or sensor is inserted into the pipe, rather than being installed inline with the pipeline. It offers easier installation and maintenance compared to full-bore meters while maintaining good accuracy in most applications.

Insertion Flow Meter Components
Let’s examine how insertion meters differ from other types:
Comparison of Flow Meter Types
| Feature | Insertion Meter | Inline Meter |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | Through pipe wall | Pipeline connection |
| Maintenance | Easier (can be removed) | Full pipe disassembly |
| Accuracy | ±2-5% typical | ±0.5-2% typical |
| Cost | Lower (material saving) | Higher |
| Pressure drop | Minimal | Significant |
| Pipe size range | 2" to very large | Typically smaller pipes |
How Should a Flow Meter Be Installed?
Professional installation follows systematic steps.
For proper installation: first prepare the site by cleaning the pipe surface, then drill the correct size hole, mount the insertion fitting, carefully insert the probe to specified depth while maintaining proper alignment, secure all connections, and finally verify the installation with field tests.
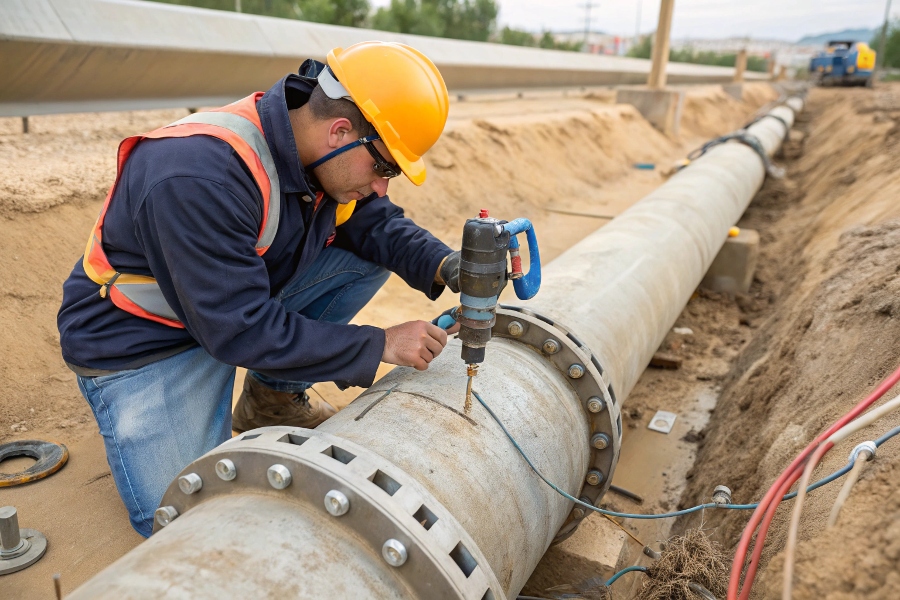

Flow Meter Installation Procedure
Let’s break down the installation sequence:
Step-by-Step Installation Guide
| Step | Action | Importance | Tools Needed |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Site selection | Affects accuracy | Pipe measurement tools |
| 2 | Surface preparation | Ensures leak-free seal | Pipe cleaner, sander |
| 3 | Hole drilling | Proper size critical | Hole saw, drill |
| 4 | Fitting installation | Structural integrity | Wrenches, sealants |
| 5 | Probe insertion | Accuracy depends on depth | Depth gauge, alignment tool |
| 6 | Electrical connections | Signal reliability | Multimeter, screwdriver |
| 7 | System verification | Confirms proper working | Process fluid, test gear |
What Is the Difference Between Inline and Insertion Flow Meter?
Key distinctions affect your choice.
The main differences are: inline meters connect between pipe flanges (requiring pipe cutting) and measure full flow, while insertion meters mount through the pipe wall (minimal disruption) and measure flow at a point that represents the whole. Insertion types offer easier retrofitting and lower pressure drop.
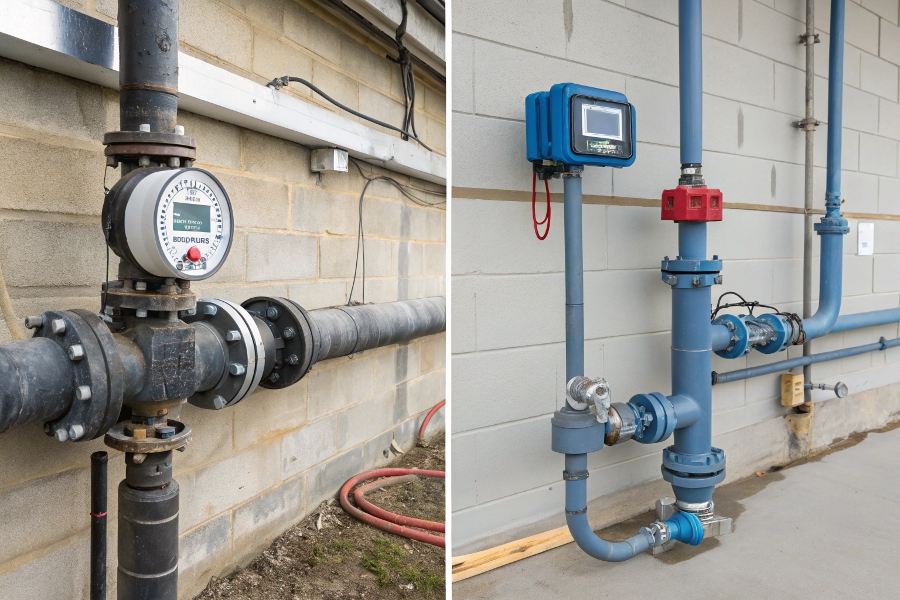
Inline Versus Insertion Flow Meters
Here’s a detailed comparison of their characteristics:
Technical Comparison Table
| Characteristic | Insertion Meter | Inline Meter |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | Hot-tap possible | Requires pipe shutdown |
| Maintenance | Probe can be removed separately | Entire unit must be removed |
| Accuracy | Slightly lower (velocity profile based) | Higher (full bore measurement) |
| Pipe Stress | Minimal | Significant (flange connections) |
| Cost (large pipes) | Much lower | Prohibitively expensive |
| Calibration | More frequent needed | Longer calibration intervals |
| Typical Applications | Large pipes, retrofit situations | Small pipes, new installations |
What Is the Rule of Thumb for Flow Meter Installation?
Professional guidelines to remember.
Key rules: 1) Allow 10 pipe diameters straight run upstream and 5 downstream, 2) Install in rising pipe sections for liquids, 3) For steam/gas, mount horizontally, 4) Keep away from pumps/valves, and 5) Ensure meter orientation matches flow direction – these fundamental rules maintain measurement accuracy.
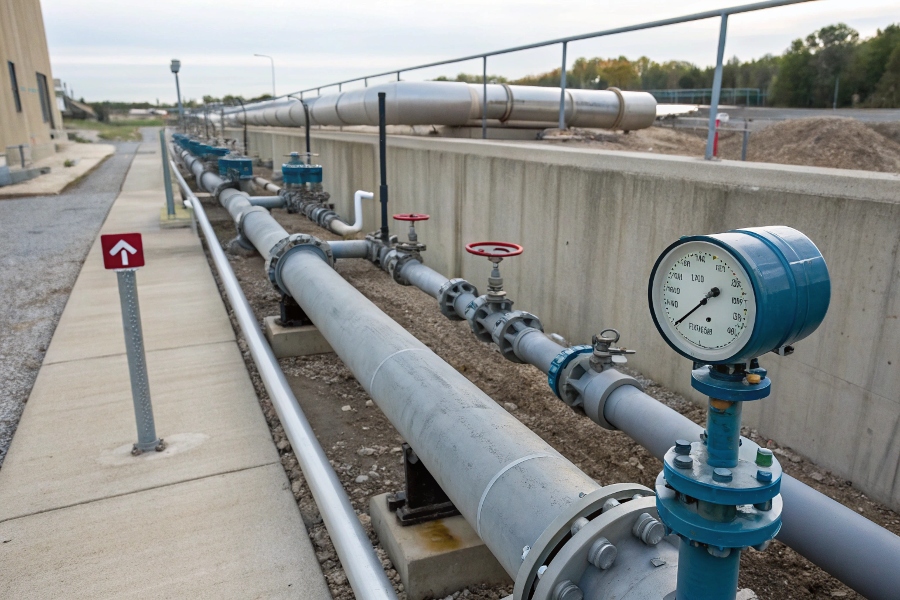

Flow Meter Installation Guidelines
These golden rules have proven their worth in the field:
Installation Rule Cheat Sheet
| Rule | Reason | Exception Cases |
|---|---|---|
| 10D upstream, 5D downstream | Minimizes flow disturbances | Laminar flow may need more |
| Avoid pipe top for liquids | Prevents air bubble interference | Gas measurement |
| Rising pipe sections preferred | Keeps pipe full | Impossible in some installations |
| Horizontal mount for steam | Prevents condensate buildup | Special steam designs |
| Proper grounding essential | Eliminates electrical noise | Non-conductive pipe solutions |
| Follow flow direction arrows | Ensures proper metering | Bidirectional flow meters |
Conclusion
Precise installation of insertion flow meters requires understanding the technology, following proper procedures, recognizing advantages over inline types, and adhering to proven installation rules – doing this right ensures accurate, reliable flow measurement for years to come.



