Improper irrigation flow measurement can result in water waste, damaged crops, and inflated utility bills.
An irrigation flow meter monitors water usage in agricultural and landscaping systems, typically measuring in gallons per minute (GPM) or cubic feet per second (CFS).
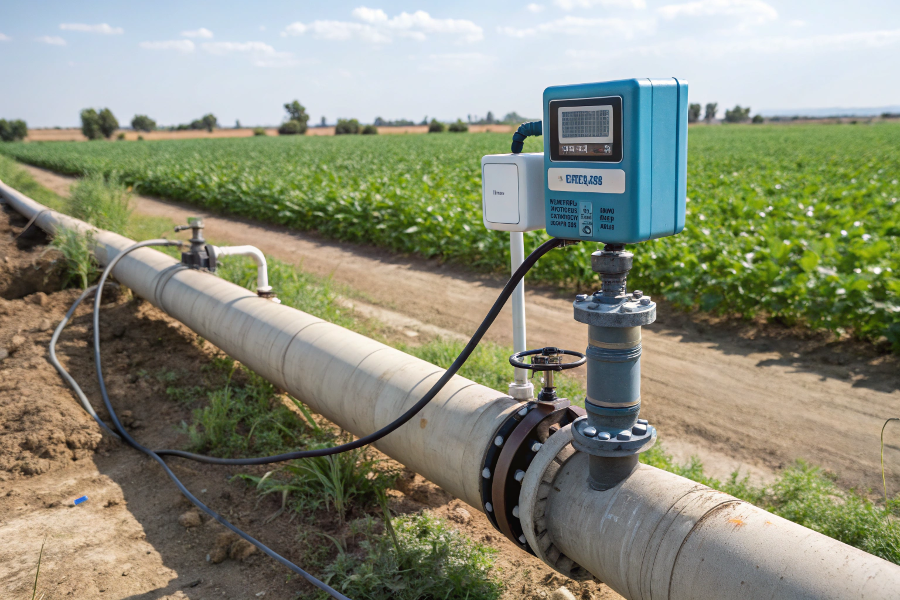

Irrigation Flow Meter System Overview
Let me share my expertise in irrigation flow measurement to help you make informed decisions.
What is an Irrigation Flow Meter?
Many farmers and landscapers struggle with water management due to inadequate flow monitoring.
Irrigation flow meters are specialized devices that measure water flow in irrigation systems, helping monitor usage, detect leaks, and optimize water distribution.
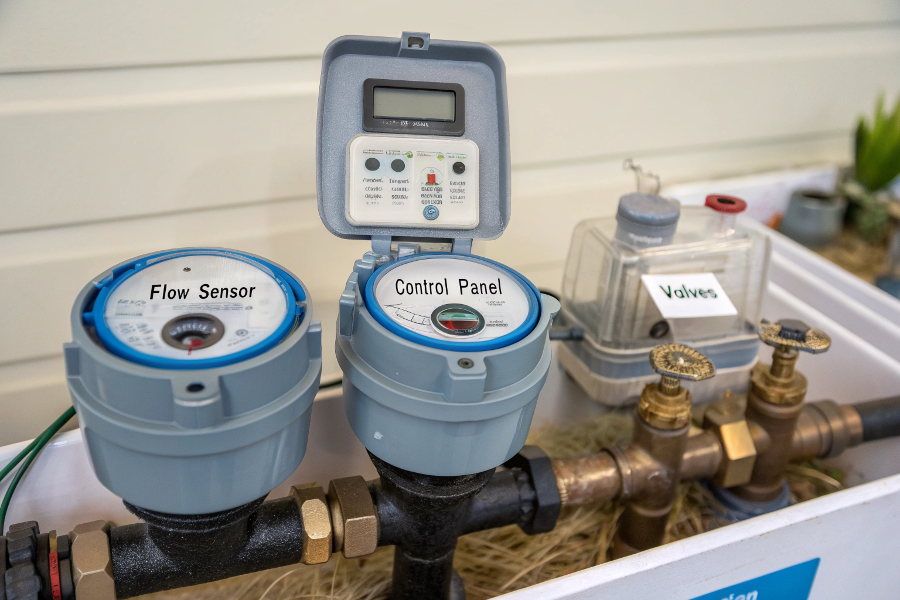

Irrigation Flow Meter Components
Based on my field experience:
Types of Irrigation Flow Meters
Common Technologies
Type Best Use Advantages Propeller Large systems Cost-effective Magnetic Clean water No moving parts Ultrasonic Modern systems Non-invasive Mechanical Small systems Simple operation Key Features
- Weather resistance
- Remote monitoring
- Data logging
- Battery life
Selection Guidelines
System Requirements
- Flow range needs
- Pressure conditions
- Installation space
- Power availability
Environmental Factors
- Water quality
- Temperature range
- Humidity levels
- UV exposure
Proper selection ensures reliability.
What is the Ideal GPM for Irrigation System?
System pressure and coverage area often confuse irrigation system designers.
Ideal irrigation flow rates typically range from 6-12 GPM for residential systems to 20-100 GPM for commercial applications, depending on coverage area.

Irrigation Flow Rate Guidelines
From my system design experience:
Flow Rate Guidelines
Application-based Rates
Application GPM Range Coverage Area Residential 6-12 Up to 1 acre Commercial 20-100 1-5 acres Agricultural 100-500 5+ acres Golf Course 200-1000 Full course Sizing Factors
- Sprinkler types
- Soil conditions
- Plant requirements
- Climate factors
System Design
Planning Considerations
- Zone division
- Pressure requirements
- Water availability
- Future expansion
Performance Factors
- Distribution uniformity
- Application rate
- Operating pressure
- System efficiency
Proper sizing ensures coverage.
Is it Worth Getting a Separate Water Meter for an Irrigation System?
High water bills and unclear usage patterns frustrate many property owners.
A separate irrigation meter is often worth the investment as it can reduce sewer charges, provide accurate usage data, and help identify system problems.
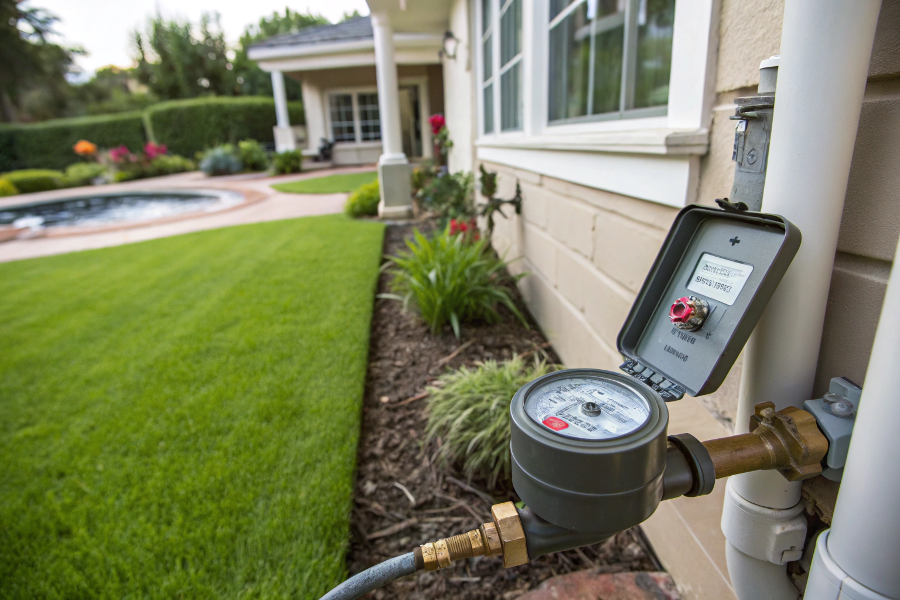

Benefits of Separate Irrigation Meters
Here’s what I’ve learned:
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Financial Considerations
Factor Impact Savings Potential Sewer Charges Eliminated 30-50% Usage Monitoring Improved 10-20% Leak Detection Enhanced 5-15% System Control Better Varies Installation Factors
- Initial cost
- Permit requirements
- Labor expenses
- Maintenance needs
Implementation Benefits
Operational Advantages
- Usage tracking
- Problem detection
- System optimization
- Cost allocation
Management Benefits
- Better planning
- Water conservation
- Budget control
- Compliance tracking
Separate meters improve management.
What Flow Rate Do I Need for Irrigation?
Determining the right flow rate challenges many system designers.
Required flow rates depend on irrigated area, plant types, and climate, typically ranging from 0.1-0.3 GPM per 100 square feet for spray systems.
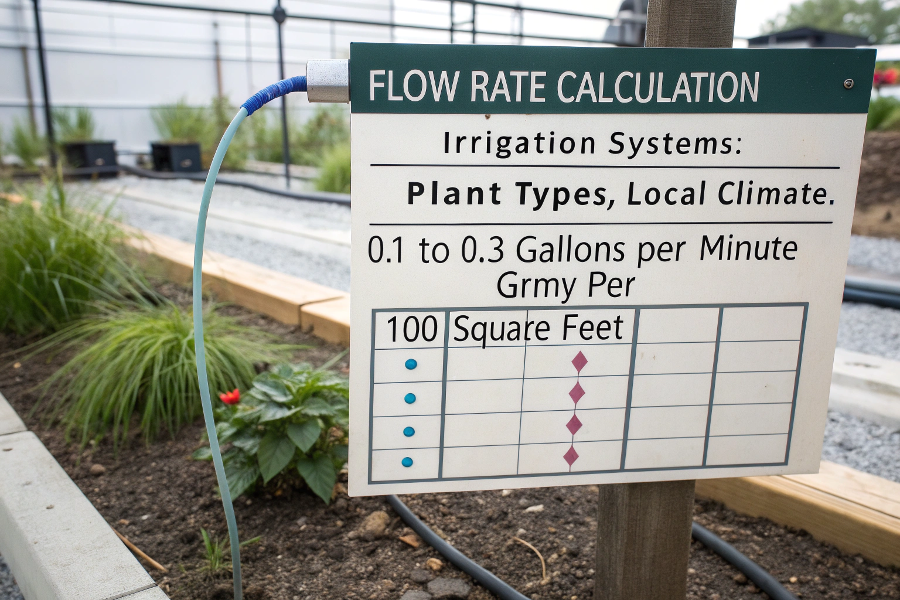
Irrigation Flow Rate Calculation Guide
From my design experience:
Flow Rate Determination
Coverage Requirements
Area Type GPM/100 sq ft Notes Lawn 0.2-0.3 Full coverage Garden 0.1-0.2 Targeted Shrubs 0.15-0.25 Drip system Trees 0.3-0.4 Deep watering Calculation Factors
- Soil type
- Plant needs
- Climate conditions
- Watering schedule
System Implementation
Design Considerations
- Zone layout
- Pressure requirements
- Equipment selection
- Control strategy
Operational Factors
- Run time calculation
- Schedule optimization
- Maintenance planning
- System monitoring
Proper flow ensures efficiency.
Conclusion
Selecting appropriate flow meters and rates for irrigation systems requires careful consideration of system size, application type, and water management needs to achieve optimal performance.



