Flow meter failures and inaccurate measurements often stem from choosing the wrong liner material for your application.
A flow meter liner is a protective inner coating that isolates the flow meter’s measuring elements from the fluid, commonly made from materials like PTFE, PFA, or rubber.

Flow Meter Liner Construction
Let me share what I’ve learned about liner materials through years of flow meter installations and troubleshooting.
What is the Liner in a Flowmeter?
Chemical compatibility issues with incorrect liner choices can lead to costly meter damage and production downtime.
The liner is a protective barrier inside the flow meter that prevents corrosion, ensures measurement accuracy, and maintains fluid purity while providing electrical insulation in electromagnetic meters.
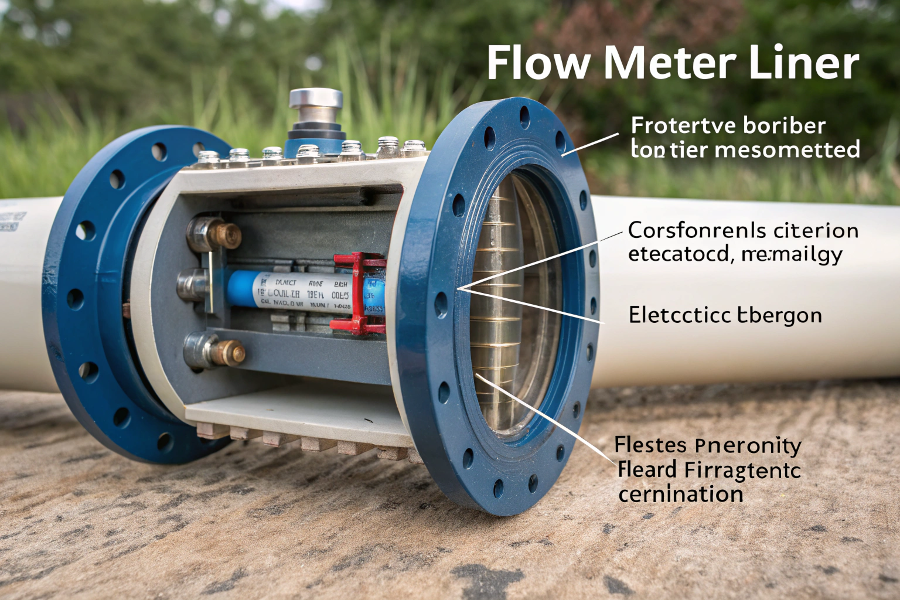
Flow Meter Liner Cross Section
From my experience with various applications:
Liner Functions
Protection Requirements
Function Purpose Benefit Chemical Resistance Prevent corrosion Extended life Electrical Insulation Signal integrity Accurate measurement Flow Profile Smooth surface Better accuracy Temperature Stability Dimensional stability Reliable operation Critical Properties
- Chemical compatibility
- Temperature resistance
- Abrasion resistance
- Pressure rating
Common Applications
Industry Specific
- Chemical processing
- Food and beverage
- Water treatment
- Mining operations
Selection Criteria
- Process conditions
- Fluid properties
- Cost considerations
- Maintenance requirements
Proper liner selection ensures longevity.
What are Flowmeters Made of?
Using inappropriate materials in flow meter construction can result in premature failure and contamination risks.
Flow meters are constructed from various materials including stainless steel, carbon steel, PVC, and specialized alloys, with internal components made from ceramics, plastics, and composite materials.
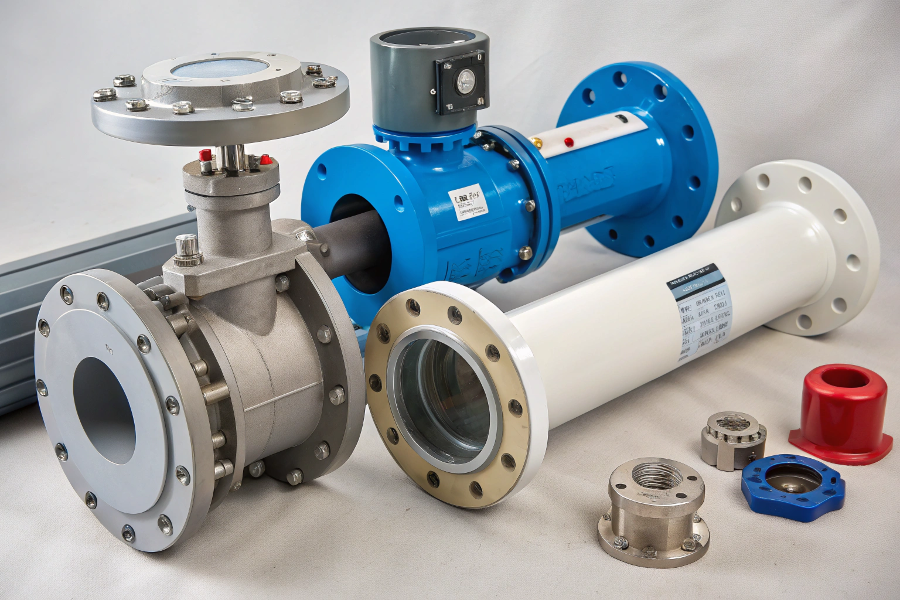

Flow Meter Material Components
Based on my manufacturing knowledge:
Material Selection
Component Materials
Component Common Materials Application Body SS316, Carbon Steel Main structure Liner PTFE, PFA, Rubber Protection Electrodes Platinum, Tantalum Sensing Seals EPDM, Viton Containment Environmental Factors
- Process temperature
- Chemical exposure
- Pressure requirements
- Wear resistance
Construction Methods
Manufacturing Process
- Casting
- Machining
- Injection molding
- Assembly techniques
Quality Control
- Material testing
- Pressure testing
- Calibration
- Documentation
Material choice impacts performance.
What is the Full Form of PTFE in Flow Meter?
Misunderstanding PTFE properties can lead to improper application and reduced meter performance.
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is a synthetic fluoropolymer widely used in flow meter liners due to its excellent chemical resistance and non-stick properties.

PTFE Chemical Structure
Here’s what I’ve learned about PTFE:
PTFE Characteristics
Key Properties
Property Value Benefit Temperature Range -100°C to 260°C Wide application Chemical Resistance Excellent Universal use Surface Friction Very low Flow efficiency Dielectric Strength High Good insulation Application Benefits
- Chemical inertness
- Temperature stability
- Non-stick surface
- Low maintenance
Performance Factors
Operating Conditions
- Temperature limits
- Pressure constraints
- Flow characteristics
- Installation requirements
Maintenance Aspects
- Cleaning procedures
- Inspection intervals
- Replacement criteria
- Troubleshooting guides
PTFE ensures reliable operation.
What is a Linear Flow Meter?
Confusion about linear flow meters often results in incorrect meter selection and poor measurement accuracy.
A linear flow meter provides direct proportional output relative to flow rate, maintaining consistent accuracy across its measuring range without the need for complex compensation.

Linear Flow Meter Operation
From my design experience:
Linear Performance
Operating Principles
Aspect Description Advantage Response Direct proportional Simple calibration Range Wide turndown Flexibility Accuracy Consistent Reliable data Output Straightforward Easy integration Design Features
- Simple construction
- Minimal maintenance
- Stable calibration
- Easy troubleshooting
Application Guidelines
Selection Criteria
- Flow range requirements
- Accuracy needs
- Installation constraints
- Budget considerations
Implementation
- Proper sizing
- Correct installation
- Regular calibration
- Performance monitoring
Linear response ensures simplicity.
Conclusion
Understanding flow meter liner materials and construction is crucial for selecting the right meter for your application, ensuring long-term reliability and accurate measurements.



