Last week, a water treatment plant lost thousands of dollars due to inaccurate measurements. The cause? Common installation mistakes that could have been easily avoided.
The most common electromagnetic flow meter installation mistakes include insufficient straight pipe runs, poor grounding, improper pipe filling, and incorrect material selection.
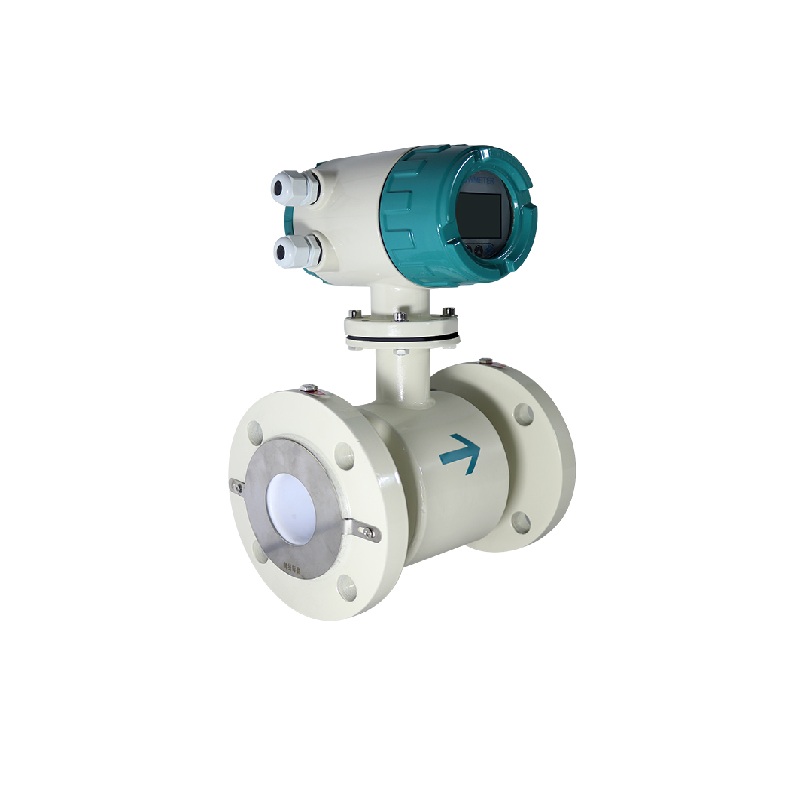

Electromagnetic Flow Meter
Through my years of experience helping customers troubleshoot their flow measurement issues, I’ve identified these critical mistakes and their solutions.
How Do Straight Pipe Requirements Affect Accuracy?
I recently helped a chemical plant improve their measurement accuracy by 25% simply by correcting their straight pipe configuration.
Electromagnetic flow meters require minimum straight pipe runs of 5 diameters upstream and 3 diameters downstream to ensure accurate measurements.
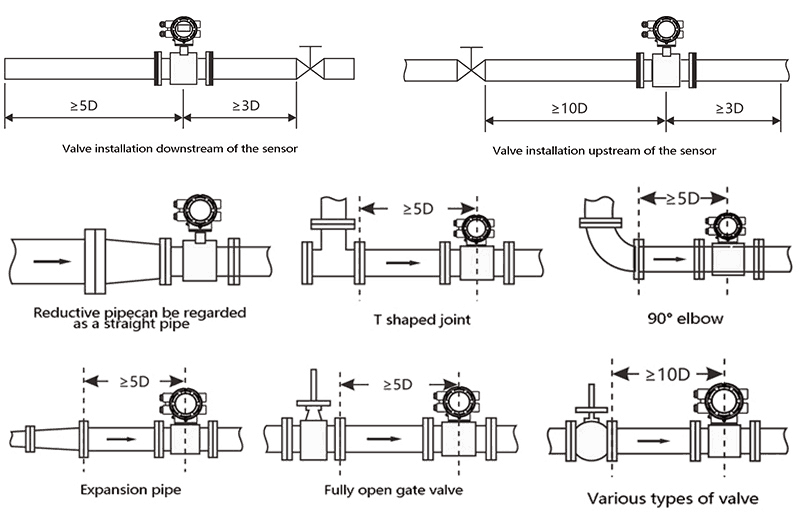
Straight Pipe Requirements
Understanding Flow Profile Impact
The importance of straight pipe runs cannot be overstated. In my experience working with various installations, I’ve observed how different upstream disturbances affect measurement accuracy:
Flow Disturbance Effects
Disturbance Type Impact on Accuracy Required Upstream Length Solution 90° Elbow Up to 8% error 10D minimum Extended straight run Double Bend Up to 15% error 15D minimum Flow straightener Valve Up to 25% error 20D minimum Relocate meter Pump Up to 30% error 25D minimum Add straight section
When space is limited, I often recommend flow conditioners or meter relocations. Last year, I helped a facility reduce their measurement error from 12% to less than 1% by implementing these solutions.
Why Is EMI Protection Critical for Installation?
A food processing plant once experienced mysterious measurement fluctuations until we discovered their flow meter was installed near a large motor.
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) can significantly affect measurement accuracy. Proper shielding, grounding, and location selection are essential for protection.
EMI Protection Methods
EMI Prevention Strategies
Based on numerous troubleshooting experiences, I’ve developed a comprehensive approach to EMI protection:
EMI Sources and Solutions
Source Potential Impact Protection Method Implementation VFDs Signal noise Shielded cables1 Double shield Motors Reading fluctuation Distance separation2 Min. 3m away Power lines Zero drift Grounding rings Both ends Welding False readings Isolation Separate conduit
Remember, proper grounding is critical. I’ve seen installations where poor grounding alone caused up to 20% measurement errors.
How Does Pipe Material Selection Impact Performance?
During a recent plant audit, I discovered their stainless steel pipe section was too short, causing significant grounding issues.
Proper pipe material and length selection ensures good electrical conductivity and accurate measurements. Non-conductive pipes require grounding rings.

Pipe Material Selection Guide
Material Compatibility Guide
Through extensive field experience, I’ve compiled this essential guide:
Material Requirements
Material Type Conductivity Required Setup Common Issues Metal Good Standard ground Length too short Plastic None Grounding rings Poor connection Lined Variable Special rings Liner damage Composite Poor Full rings Contact problems
Additional considerations include temperature resistance, chemical compatibility, and pressure ratings. I always recommend reviewing these factors during the design phase.
What Ensures Complete Pipe Filling?
Empty pipe detection errors are among the most common issues I encounter during site visits.
Partially filled pipes can cause significant measurement errors. Proper installation orientation and empty pipe detection are crucial.
Pipe Filling Solutions
Filling Assurance Methods
Based on countless installations, here are the most effective solutions:
Installation Configurations
Method Application Effectiveness Implementation Vertical up Best practice Very high Preferred U-section Space limited High Alternative Reduction Large pipes Medium Last resort Horizontal With slope Variable Careful check
These solutions have helped me resolve filling issues in numerous installations, improving measurement reliability by up to 100%.
How Do You Match Flow Meter to Process Conditions?
A recent consulting case showed how improper sizing led to a 40% overestimation of flow rates.
Matching flow meter specifications to process conditions ensures optimal performance. Consider flow range, pressure, temperature, and conductivity.
Process Condition Matching
Process Compatibility Analysis
My experience with various applications has shown these critical factors:
Selection Criteria
Parameter Range Consideration Impact Flow rate 0.3-10 m/s Sizing Accuracy Pressure Process max Rating Safety Temperature Process range Materials Longevity Conductivity >5µS/cm Fluid type Operation
Proper matching has helped my clients achieve measurement accuracies better than 0.5% in most applications.
Conclusion
Avoiding these common installation mistakes can significantly improve electromagnetic flow meter performance and reliability. Proper planning and attention to detail during installation are essential.
Need expert guidance for your electromagnetic flow meter installation? Contact our technical team for professional support.



