Many process engineers struggle with understanding how DP transmitters can accurately measure flow rates.
A DP transmitter measures flow by calculating the pressure difference between two points in a pipe using a primary element (like an orifice plate), converting this pressure drop into flow rate using the square root relationship.
 >
>
DP Flow Measurement Principle
Let me share our practical experience with DP flow measurement systems.
How Does A DP Transmitter Measure Flow?
Incorrect setup of DP flow measurement systems can lead to significant measurement errors.
DP transmitters measure flow by detecting the pressure difference created by a flow restriction, using the principle that flow rate is proportional to the square root of the differential pressure.

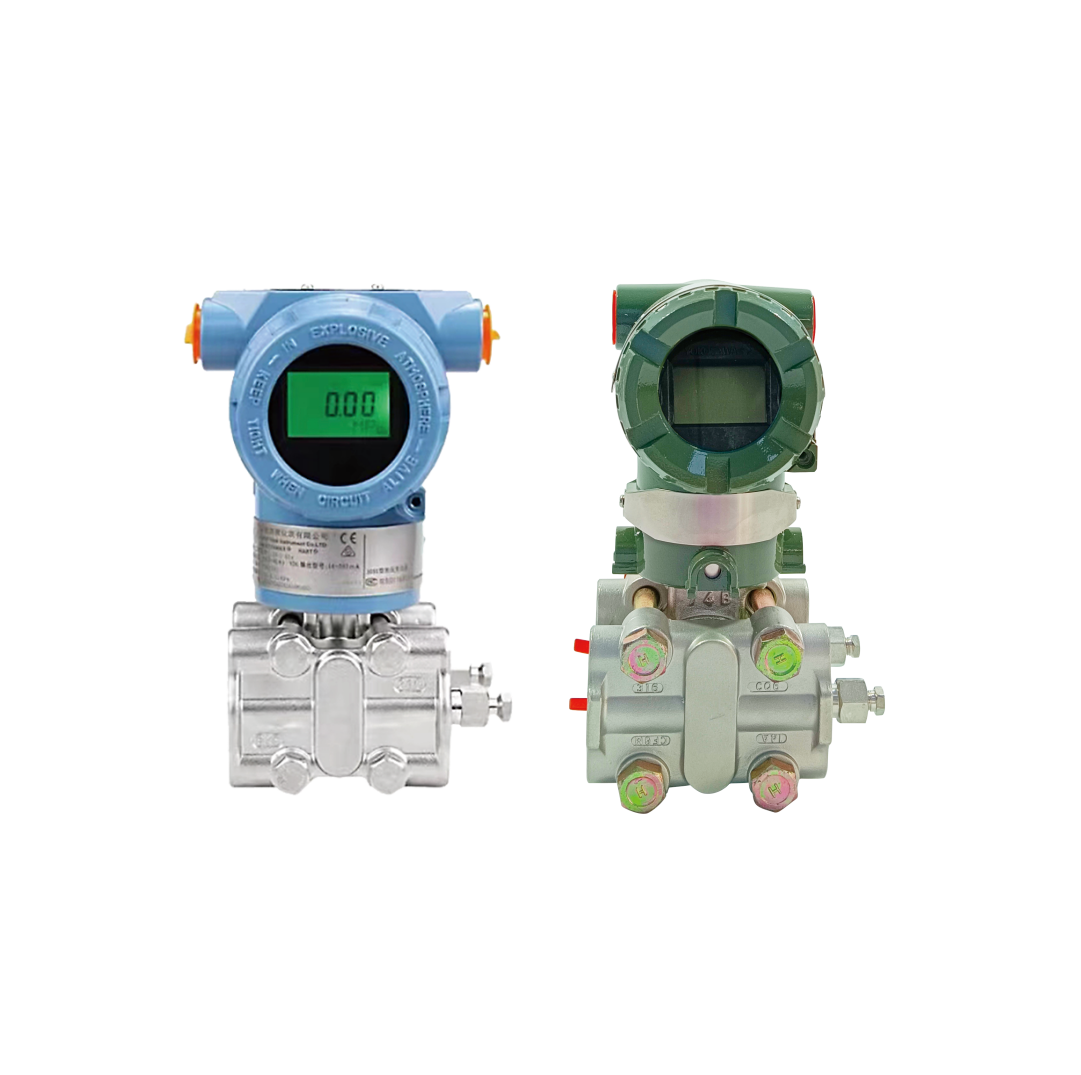
DP Flow Measurement Setup
From our field experience:
Measurement Principles
Key Components
Component Function Considerations Primary Element Flow restriction Type selection Impulse Lines Pressure transfer Installation DP Transmitter Measurement Calibration Flow Computer Calculation Configuration Operating Factors
- Fluid properties
- Process conditions
- Installation requirements
- Maintenance needs
System Implementation
Design Considerations
- Flow range
- Pressure loss
- Accuracy requirements
- Environmental conditions
Installation Requirements
- Straight pipe runs
- Mounting position
- Impulse line layout
- Access for maintenance
What Is A Differential Pressure Sensor For Flow Measurement?
Understanding the right sensor type is crucial for accurate flow measurement.
A differential pressure sensor for flow measurement is a device that measures the pressure difference across a flow restriction, typically using a diaphragm or capacitive sensing element.
Based on our technical expertise:
Sensor Technologies
Common Types
Type Operation Application Capacitive Diaphragm deflection Clean fluids Piezoresistive Strain measurement High pressure Silicon MEMS technology Precise measurement Resonant Frequency change High stability Selection Criteria
- Process fluid
- Pressure range
- Temperature limits
- Material compatibility
Performance Factors
Operational Considerations
- Response time
- Stability
- Accuracy needs
- Maintenance requirements
Environmental Effects
- Temperature
- Vibration
- EMI/RFI
- Humidity
How To Calculate Flow With Differential Pressure?
Many engineers find flow calculations from DP measurements challenging.
Calculate flow using the formula Q = K√ΔP, where Q is flow rate, K is the flow coefficient determined by the primary element, and ΔP is the measured differential pressure.
Flow Calculation Methods
Drawing from our calculation experience:
Calculation Process
Basic Parameters
Parameter Symbol Units Flow Rate Q m³/h or GPM Flow Coefficient K Varies Differential Pressure ΔP inH2O or mbar Fluid Density ρ kg/m³ Correction Factors
- Temperature
- Pressure
- Compressibility
- Reynolds number
Implementation Steps
Design Calculations
- Primary device sizing
- Range determination
- Accuracy analysis
- Pressure loss calculation
Field Verification
- Initial setup
- Zero checking
- Span verification
- Performance validation
How To Measure Flow With DPT?
Setting up a DP transmitter for flow measurement requires careful attention to detail.
Measure flow with a DPT by installing a primary element, connecting impulse lines properly, configuring the transmitter with correct parameters, and maintaining regular calibration.
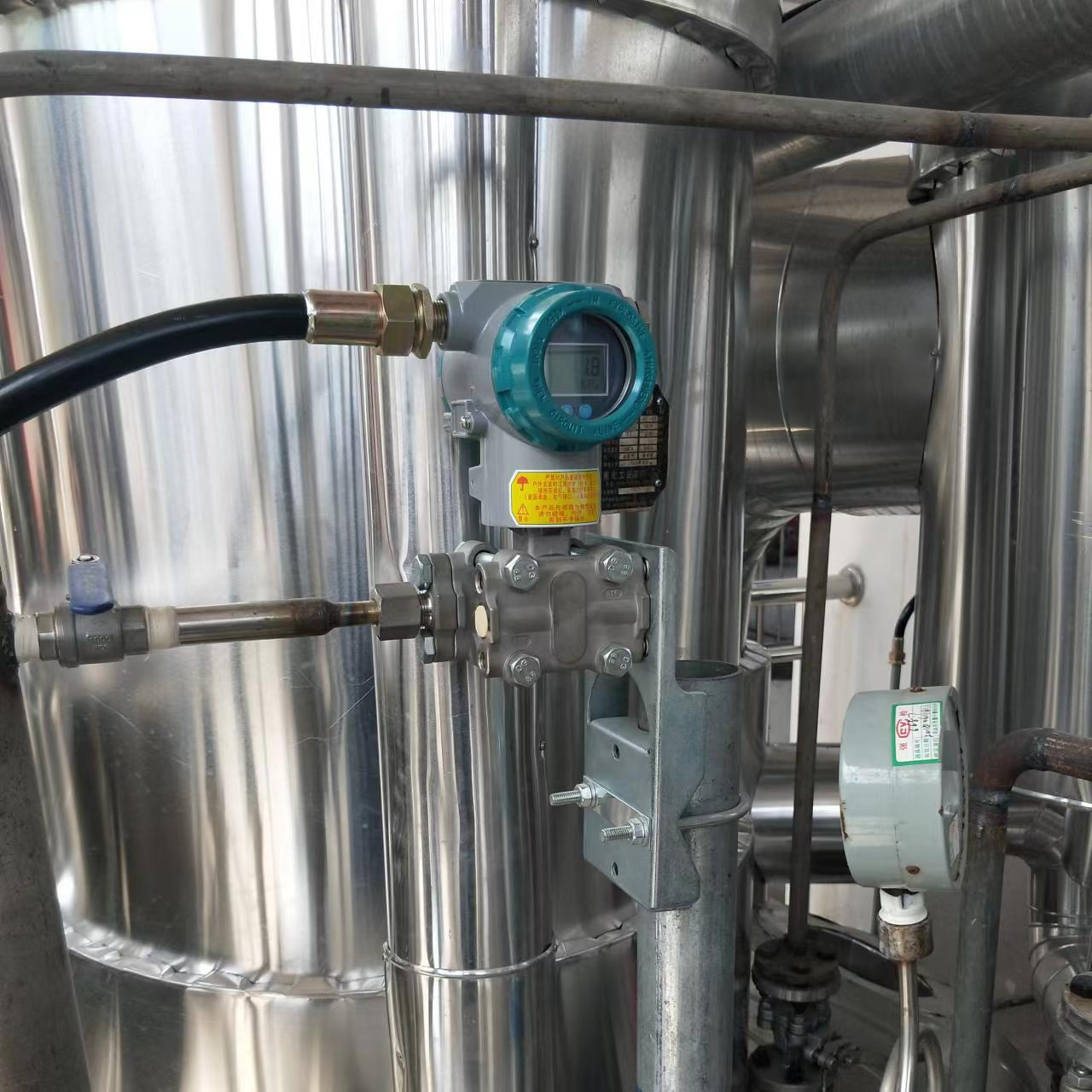

DPT Flow Measurement Setup
Based on our installation experience:
Setup Requirements
Installation Steps
Step Action Purpose Primary Element Install restriction Create DP Impulse Lines Connect properly Transfer pressure Transmitter Mount and wire Measure DP Configuration Set parameters Calculate flow Best Practices
- Proper orientation
- Air purging
- Zero checking
- Regular maintenance
System Optimization
Performance Factors
- Signal stability
- Response time
- Accuracy needs
- Range turndown
Maintenance Requirements
- Regular calibration
- Impulse line cleaning
- Zero verification
- Documentation
Conclusion
Successful DP flow measurement depends on proper understanding of principles, correct installation, accurate calculations, and regular maintenance to ensure reliable performance.



