Many process engineers struggle with flow measurement accuracy because they don’t understand the importance of K-factor calibration.
K-factor is a calibration constant that represents the number of pulses a flow meter generates per unit volume of fluid, typically expressed as pulses per gallon or liter.
Flow Meter K-Factor Explanation
Let me share my experience with K-factor calibration and its impact on measurement accuracy.
What is the K-factor of a Flow Meter?
Incorrect K-factor settings lead to measurement errors that can cost thousands in product loss or billing discrepancies.
A flow meter’s K-factor is the number of electronic pulses it produces for each volumetric unit of fluid passing through it, commonly ranging from 100 to 10,000 pulses per gallon.

K-Factor Measurement Process
From my calibration experience:
K-Factor Determination
Measurement Basics
Meter Size Typical K-Factor Range Resolution 1/2 inch 8000-12000 ppg ±0.5% 1 inch 4000-8000 ppg ±0.3% 2 inch 1000-4000 ppg ±0.2% 4 inch 100-1000 ppg ±0.1% Influencing Factors
- Meter design
- Flow range
- Fluid properties
- Operating conditions
Calibration Process
Standard Methods
- Laboratory calibration
- Field verification
- Comparative testing
- Statistical analysis
Documentation Requirements
- Calibration certificates
- Test conditions
- Traceability records
- Uncertainty calculations
Proper calibration ensures accuracy.
What Does K-factor Mean?
Engineers often misinterpret K-factor’s significance in flow measurement systems.
K-factor represents the relationship between flow meter output signals and actual fluid volume, serving as a conversion factor for accurate flow calculation.

K-Factor Definition Diagram
Based on my technical expertise:
K-Factor Components
Signal Analysis
Component Purpose Impact Pulse count Flow detection Primary measurement Time base Rate calculation Speed reference Volume unit Standardization Conversion basis Correction factors Compensation Accuracy improvement Mathematical Relationship
- Pulse frequency
- Flow rate correlation
- Linear response
- Error analysis
Practical Applications
Usage Areas
- Custody transfer
- Process control
- Quality assurance
- Research applications
Implementation Considerations
- Signal processing
- Data conversion
- System integration
- Maintenance planning
Understanding meaning improves application.
What is the K-factor of the Flow Coefficient?
Many technicians confuse K-factor with flow coefficient, leading to calculation errors.
The flow coefficient K-factor relates actual flow rate to theoretical flow rate, considering fluid properties and system characteristics.
Flow Coefficient Calculation
Here’s what I’ve learned:
Flow Coefficient Analysis
Component Relationships
Parameter Influence Calculation Impact Pressure drop Direct Flow rate determination Fluid density Indirect Mass flow conversion Viscosity Variable Reynolds correction Temperature Indirect Property adjustment Application Factors
- System geometry
- Installation effects
- Operating conditions
- Fluid characteristics
Calculation Methods
Standard Procedures
- Theoretical analysis
- Empirical testing
- Comparative studies
- Statistical validation
Correction Requirements
- Temperature effects
- Pressure influence
- Viscosity impact
- Installation factors
Accurate coefficients ensure reliability.
What is the K-factor Correction?
Inaccurate K-factor corrections can lead to significant measurement errors and process control problems.
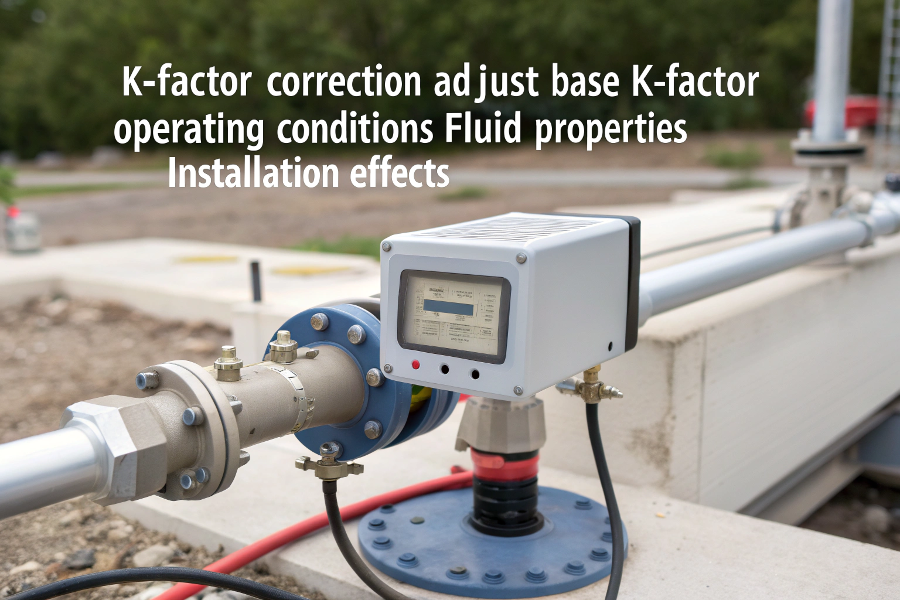
K-factor correction adjusts the base K-factor for variations in operating conditions, fluid properties, and installation effects to improve measurement accuracy.
K-Factor Correction Process
From my field experience:
Correction Procedures
Adjustment Factors
Factor Purpose Application Temperature Thermal effects Property changes Pressure Density impact Flow conditions Reynolds number Flow regime Linearity Installation Position effects System influence Implementation Steps
- Data collection
- Analysis process
- Calculation methods
- Verification procedures
Verification Process
Testing Requirements
- Standard conditions
- Operating ranges
- Accuracy needs
- Documentation requirements
Quality Assurance
- Validation methods
- Error analysis
- Performance monitoring
- Regular review
Proper correction ensures accuracy.
Conclusion
Understanding and properly applying K-factor concepts, including calibration, correction, and relationship to flow coefficients, is essential for achieving accurate flow measurements in any application.



