Incorrect flow measurement can lead to product quality issues, safety hazards, and significant financial losses in industrial processes.
Flow meters are used to measure and monitor fluid movement in pipes, essential for process control, billing, research, and safety applications across various industries.
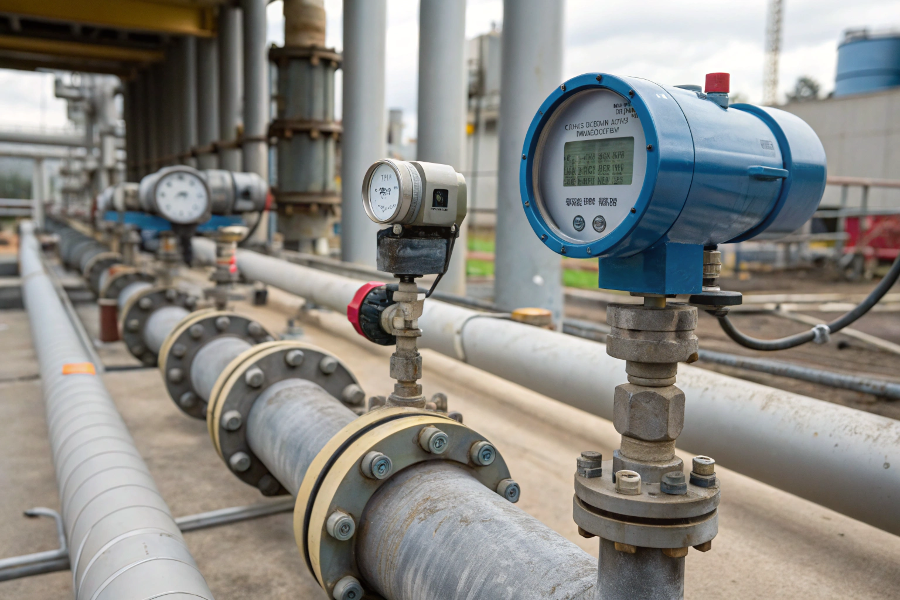

Flow Meter Industrial Applications
Let me share my experience with flow meter applications across different industries.
What is the Most Commonly Used Flow Meter?
Selecting the wrong flow meter type can result in wasted investment and unreliable measurements.
Magnetic flow meters are the most commonly used type, particularly in water and wastewater industries, due to their reliability, accuracy, and lack of moving parts.
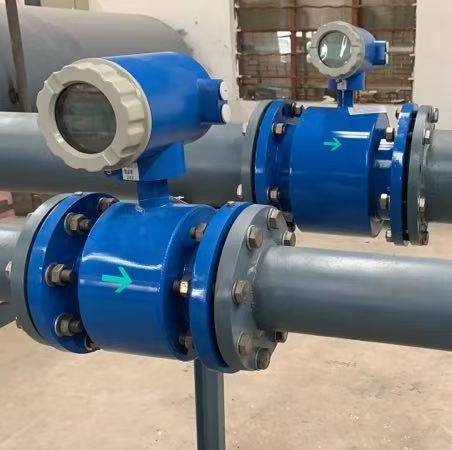

Magnetic Flow Meter Installation
Based on my industry experience:
Popular Flow Meter Types
Market Distribution
Type Usage % Main Application Magnetic 35% Water/Wastewater Coriolis 25% Oil/Gas Ultrasonic 20% Chemical Others 20% Various Selection Factors
- Process fluid
- Required accuracy
- Installation conditions
- Budget constraints
Application Areas
Industry Sectors
- Water treatment
- Chemical processing
- Food and beverage
- Pharmaceutical
Specific Uses
- Custody transfer
- Process control
- Quality assurance
- Research and development
Understanding preferences aids selection.
What Are the Reasons for a Patient to Use a Flowmeter?
Medical professionals often struggle to explain the importance of flow measurement to patients.
Medical flow meters help monitor and control oxygen delivery, measure breathing capacity, and ensure proper medication dosing for patient treatment and recovery.
Medical Flow Meter Applications
From my medical industry experience:
Medical Applications
Common Uses
Purpose Device Type Benefit Oxygen therapy Gas flowmeter Proper dosing Spirometry Peak flow meter Lung function IV delivery Liquid flowmeter Medication control Anesthesia Gas mixer Safe sedation Patient Benefits
- Treatment monitoring
- Recovery tracking
- Disease management
- Safety assurance
Clinical Requirements
Key Features
- Easy reading
- Quick response
- High accuracy
- Simple operation
Safety Considerations
- Sterilization needs
- Material compatibility
- Error prevention
- Alarm systems
Patient safety drives design.
What Do Most Flow Meters Test For?
Understanding flow measurement parameters is crucial for proper meter selection and use.
Flow meters primarily test for volumetric flow rate, mass flow rate, flow velocity, and total flow volume, depending on the application requirements.
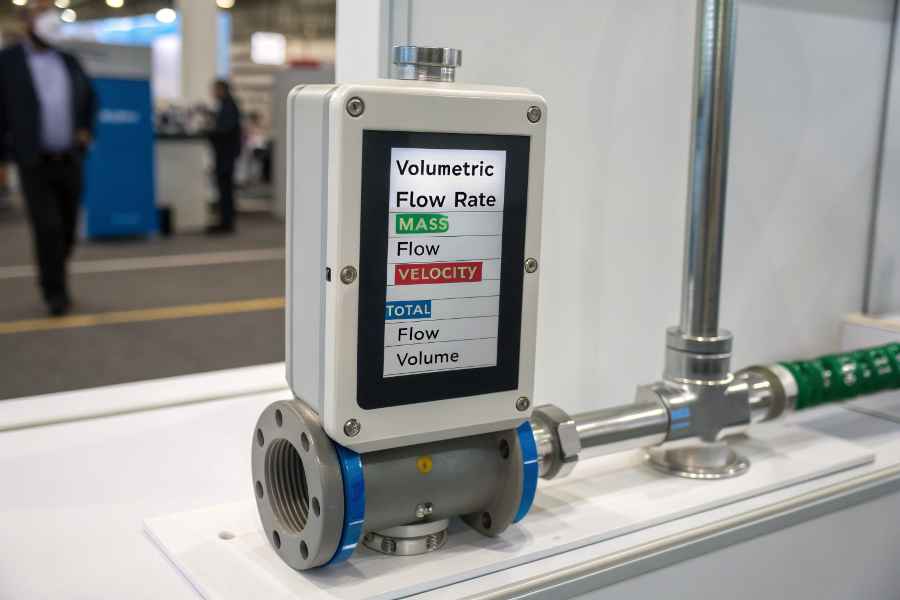

Flow Measurement Parameters
Here’s what I’ve learned:
Measurement Parameters
Primary Measurements
Parameter Unit Application Volume flow GPM/LPM Water systems Mass flow kg/h Process control Velocity m/s Research Total flow Gallons/m³ Billing Secondary Parameters
- Temperature
- Pressure
- Density
- Conductivity
Testing Methods
Direct Measurement
- Physical displacement
- Time-based counting
- Weight measurement
- Volume tracking
Indirect Measurement
- Pressure differential
- Electromagnetic
- Ultrasonic signals
- Thermal properties
Parameter selection affects accuracy.
What is a Normal Flow Meter Reading?
Process operators often question whether their readings indicate normal operation.
Normal flow meter readings typically fall between 20-80% of the meter’s full scale, with specific ranges depending on application and pipe size.

Normal Flow Meter Readings
From my field experience:
Reading Guidelines
Typical Ranges
Pipe Size Normal Range Maximum Flow 1 inch 2-20 GPM 30 GPM 2 inch 5-50 GPM 80 GPM 4 inch 20-200 GPM 300 GPM 6 inch 50-500 GPM 800 GPM Influencing Factors
- Process requirements
- System design
- Operating pressure
- Fluid properties
Performance Monitoring
Critical Points
- Zero stability
- Span accuracy
- Repeatability
- Response time
Documentation Needs
- Reading logs
- Calibration records
- Maintenance history
- Trend analysis
Understanding ranges ensures proper operation.
Conclusion
Flow meters serve critical roles across industries, from industrial process control to medical applications, with selection and usage depending on specific measurement needs and operating conditions.



