Selecting the wrong level measurement technology can result in inaccurate readings, process inefficiencies, and wasted resources.
Ultrasonic level transmitters use sound waves and are ideal for simpler applications, while radar level transmitters use electromagnetic waves and excel in challenging environments. Each has distinct advantages based on application needs.
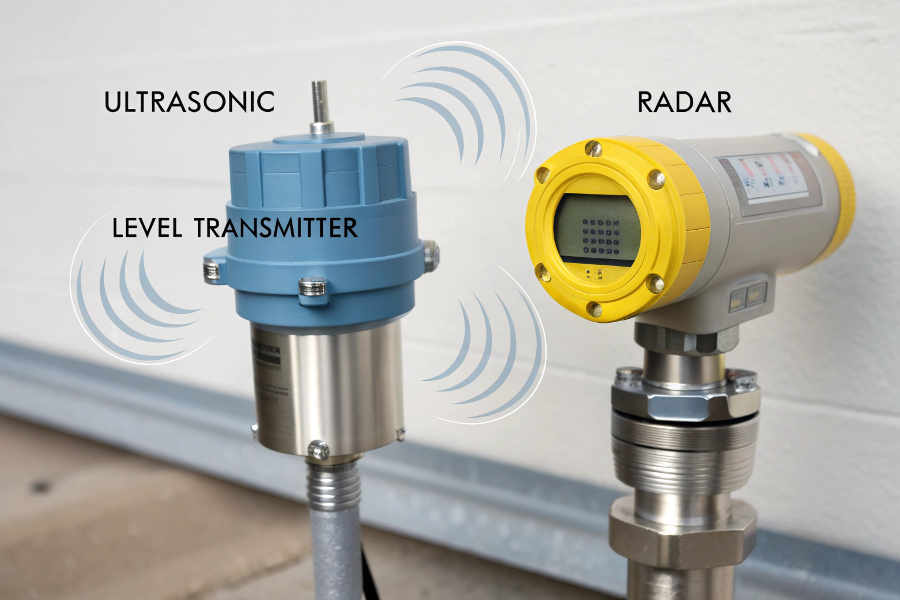

Ultrasonic vs Radar Level Transmitter Comparison
Let me share insights from my experience in implementing both technologies across various industries.
What Is the Difference Between Ultrasonic and Radar Level Transmitter?
Choosing the right technology impacts measurement accuracy and reliability.
Ultrasonic transmitters emit sound waves at 20-200 kHz and are cost-effective for simple applications, while radar transmitters use electromagnetic waves at 6-26 GHz and perform better in challenging conditions like dust, vapor, or turbulence.

Technology Differences Illustration
From my field experience, here are the key differences:
Performance Factors
Environmental Conditions
Temperature Impact
- Ultrasonic: Highly affected
- Radar: Minimal impact
Vapor/Dust
- Ultrasonic: Limited performance
- Radar: Excellent penetration
Application Considerations
Cost
- Ultrasonic: Lower initial investment
- Radar: Higher but more versatile
Accuracy
- Ultrasonic: ±0.25%
- Radar: ±0.1%
These differences help determine the best solution for specific applications.
What Is the Difference Between GWR and DP Level Transmitter?
Understanding measurement principles helps optimize technology selection.
Guided Wave Radar (GWR) uses electromagnetic waves along a probe for direct level measurement, while Differential Pressure (DP) transmitters measure level by sensing hydrostatic pressure. GWR offers higher accuracy and isn’t affected by density changes.
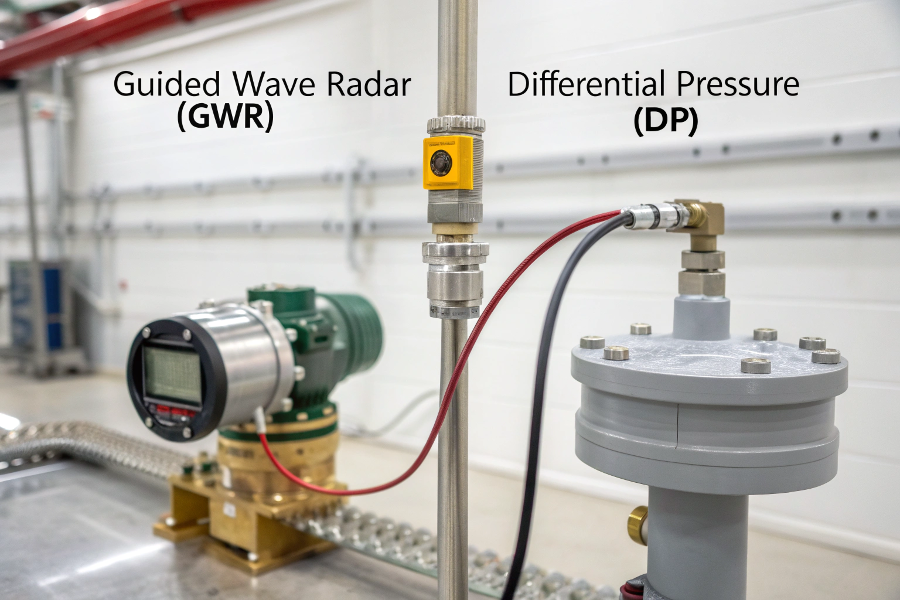
GWR vs DP Transmitter Comparison
Here’s my practical comparison:
Technical Differences
Measurement Method
- GWR: Direct level measurement
- DP: Pressure-based inference
Installation Requirements
- GWR: Probe installation
- DP: Pressure taps and impulse lines
Application Considerations
- Process conditions
- Maintenance needs
- Installation costs
- Accuracy requirements
These factors influence technology selection for specific applications.
Is Radar the Same as Ultrasonic?
Understanding fundamental differences aids technology selection.
No, radar and ultrasonic technologies differ in their operating principles. Radar uses electromagnetic waves (6-26 GHz), while ultrasonic uses sound waves (20-200 kHz), resulting in different performance characteristics.

Operating Principles Comparison
Based on my installation experience:
Key Differences
Wave Properties
- Propagation speed
- Environmental interference
- Material penetration
Application Suitability
- Process conditions
- Environmental factors
- Measurement accuracy
Performance Factors
- Temperature sensitivity
- Vapor handling
- Measurement speed
- Cost considerations
These differences determine application suitability.
How Do Ultrasonic or Radar Devices Measure Levels?
Understanding measurement principles ensures proper application.
Both technologies measure level by timing signal reflection. Ultrasonic devices emit sound waves that bounce off the material surface, while radar devices use electromagnetic waves, calculating distance based on return time.
Level Measurement Principles
From my implementation experience:
Measurement Process
Signal Transmission
- Wave generation
- Signal focusing
- Beam angle considerations
Signal Processing
- Echo detection
- Signal filtering
- Distance calculation
Influencing Factors
Physical Conditions
- Surface turbulence
- Material properties
- Tank geometry
Environmental Impact
- Temperature variations
- Pressure changes
- Atmospheric conditions
Understanding these principles helps optimize installation and operation.
Conclusion
Choosing between ultrasonic and radar level transmitters depends on application requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints. Understanding their differences and operational principles ensures optimal technology selection for specific measurement needs.



