Your mag meter was working perfectly yesterday – why is it showing erratic numbers today? Small installation oversights cause 80% of accuracy issues.
Magnetic flow meter errors stem from: 1) Improper grounding (50% of failures), 2) Partially filled pipes (air bubbles disrupt readings), 3) Electrode coating (insulating buildup blocks signals), 4) Uncalibrated zero point, 5) Strong electromagnetic interference from nearby equipment.
Let’s diagnose your specific problem systematically.
How to Troubleshoot a Magnetic Flow Meter?
Before calling technicians, try these field checks first.
Troubleshoot step-by-step: check power supply (18-30V DC), verify proper grounding (<1 ohm), inspect electrode condition (clean with toothbrush if coated), confirm fully liquid-filled pipe, test with known flow rate, and check for process noise/vibration interference.
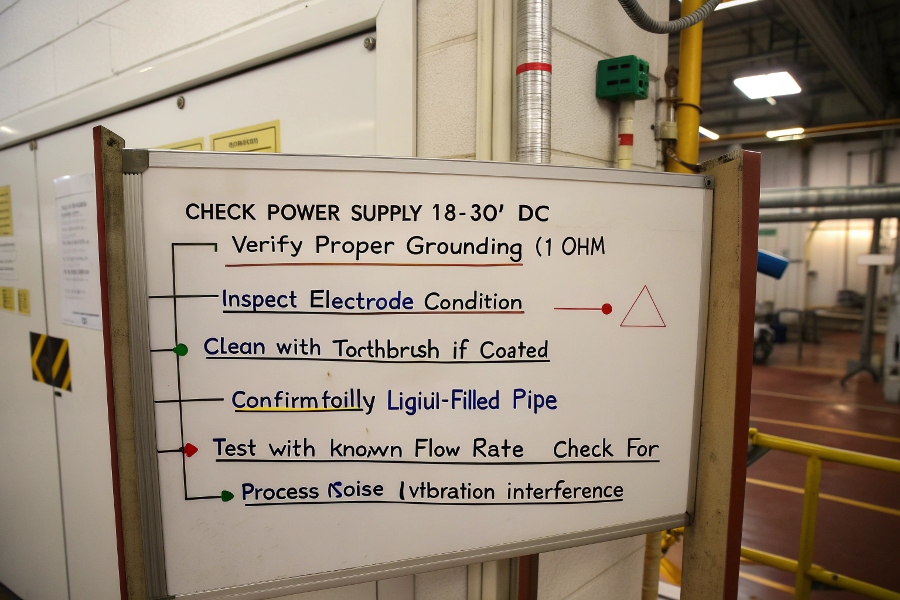
Mag Meter Diagnostic Steps
Essential diagnostic tools and methods:
Magnetic Flow Meter Troubleshooting Kit
| Tool | Purpose | Critical Specs |
|---|---|---|
| Multimeter | Ground resistance measurement | 0.1Ω resolution |
| Endoscope | Internal electrode inspection | 5mm diameter, LED light |
| Process calibrator | 4-20mA loop verification | 0.05% accuracy |
| Ultrasonic flowmeter | Cross-verification | Clamp-on type |
| pH test strips | Chemical attack detection | 0-14 range |
How to Reset Electromagnetic Flow Meter?
Resetting should be your last recourse – understand the consequences.
Factory resets erase all calibration data – only perform when: 1) Replacing electronics, 2) Corrupted software, 3) Major configuration errors. Always document existing settings (K-factor, pipe size, liner material) before resetting. For Endress+Hauser devices1, hold ▲+▼ during startup for 10 seconds.
Manufacturer-specific reset procedures:
Reset Methods for Common Mag Meters
| Manufacturer | Soft Reset | Factory Reset |
|---|---|---|
| Siemens MAG 6000 | Mode+Exit buttons 5 sec | Service password required |
| Krohne Waterflux | Quick power cycle | Ground terminal jumper |
| ABB FSM4000 | ▲▼◄► simultaneous press | Config card reload |
| Yokogawa AXFA11 | Front panel combo | Dedicated reset tool |
What Are the Sources of Error in a Flow Meter?
Not all inaccuracies originate from the meter itself.
Four error categories: 1) Installation (bent pipes, wrong orientation), 2) Process (bubbles, pulsations), 3) Environmental (temperature swings, lightning strikes), 4) Instrumentation (aging electrodes, power surges). Installation errors account for 60% of field issues – particularly insufficient straight pipe runs.

Accuracy Impact Factors
Quantified error contributors:
Typical Mag Meter Error Budget
| Error Source | Impact Range | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Flow profile | ±0.5% to ±5% | 10D upstream straight pipe |
| Electrode coating | -1% per 0.1mm coat | Regular CIP cleaning |
| Grounding | ±10% to complete fail | Separate ground rod |
| Temperature swing | ±0.1%/°C | Built-in compensation |
| Power fluctuation | ±1% per 5V change | Voltage regulator |
Why Is My Flow Meter Not Reading Correctly?
Nine out of ten "faulty meter" cases trace back to simple, fixable issues.
Quick diagnostics: 1) Check for empty pipe (listen for flow sounds), 2) Verify grounding (measure pipe-to-meter voltage <1V), 3) Observe process changes (new pumps/valves?), 4) Inspect electrodes (remove buildup with vinegar soak), 5) Confirm proper units selection (GPM vs m³/h).
Common misreading scenarios:
False Reading Analysis Guide
| Symptom | Most Likely Cause | Field Test |
|---|---|---|
| Zero drift | Grounding issue2 | Measure pipe voltage |
| Erratic spikes | Electrode coating3 | Visual inspection |
| Consistently low | Partially filled pipe | Ultrasonic verification4 |
| No signal | Power failure | Check fuse/voltage |
| Reverse flow reading | Wrong wiring | Swap sensor cables |
Installation Best Practices for Accurate Measurement
Prevention beats troubleshooting – get these right during installation.
Critical installation rules: 1) Ground rings required for non-conductive pipes, 2) Upstream straight run = 10x diameter (5x downstream), 3) Avoid vertical-down flow (causes air entrapment), 4) Isolate from vibration sources, 5) Never install after pumps/elbows without adequate straight runs.

Optimal Mag Meter Positioning
Installation verification checklist:
Post-Installation Commissioning Tests
| Test | Method | Acceptance Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Ground verification | Resistance meter | <1 ohm to earth |
| Empty pipe response | Drain system completely | ≤0.5% of full scale |
| Polarity check | Reverse flow test | Negative value shown |
| Noise immunity | Start nearby motor | <0.2% reading change |
| Process temperature | Compare with RTD reading | ±2°C agreement |
Conclusion
Magnetic flow meter errors primarily stem from installation oversights and maintenance neglect – proper grounding alone prevents half of all field issues. Regular electrode inspection and zero calibration maintain optimal accuracy between scheduled professional verifications.
Discover specific instructions for resetting Endress+Hauser devices to ensure proper functionality and avoid data loss. ↩
Understanding grounding issues is crucial for accurate measurements and preventing errors in your system. Explore this link for detailed insights. ↩
Learn how electrode coating can impact your readings and discover solutions to maintain measurement integrity. This resource is invaluable for professionals. ↩
Ultrasonic verification is a key technique for ensuring accurate measurements in partially filled pipes. Discover its applications and benefits here. ↩



