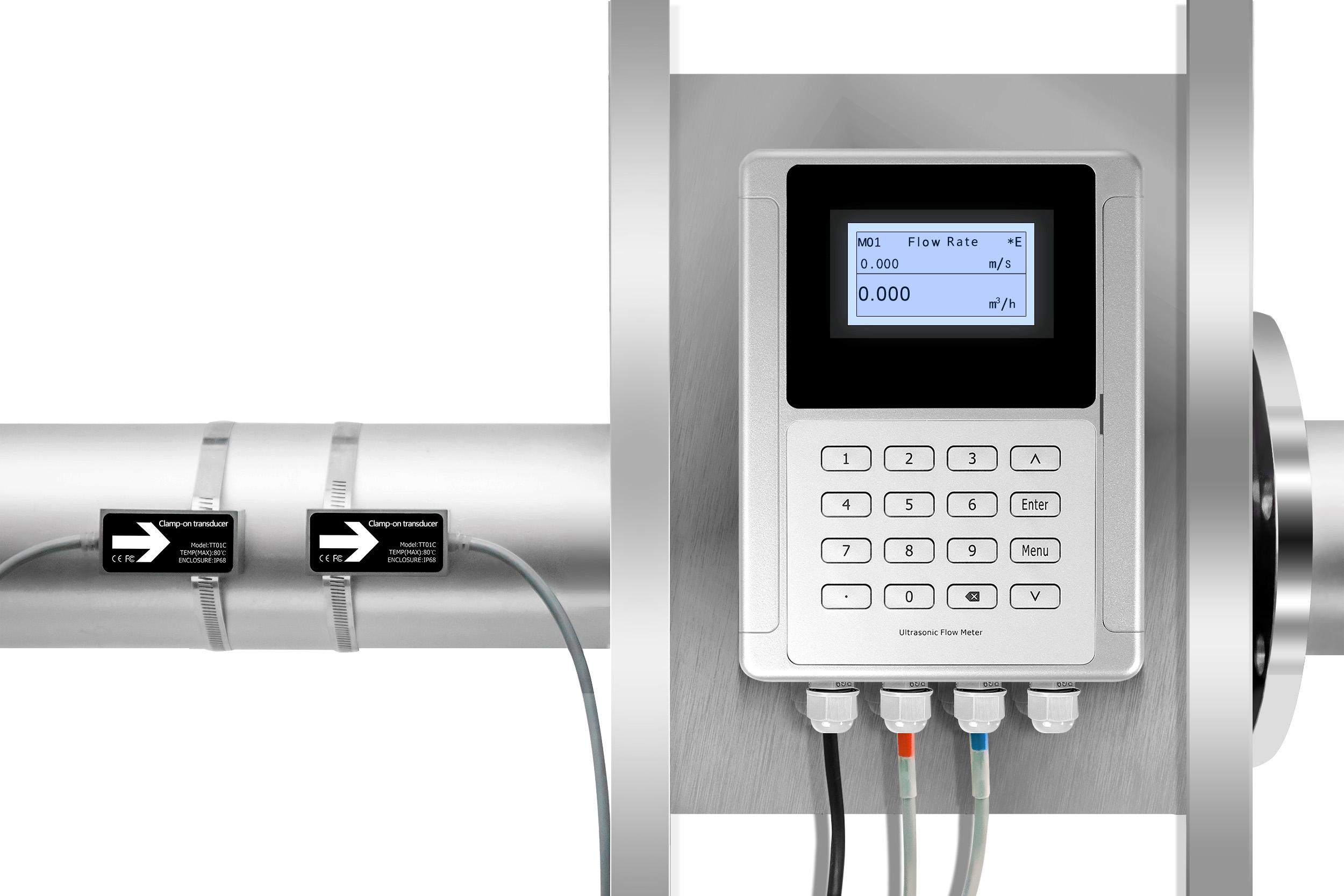
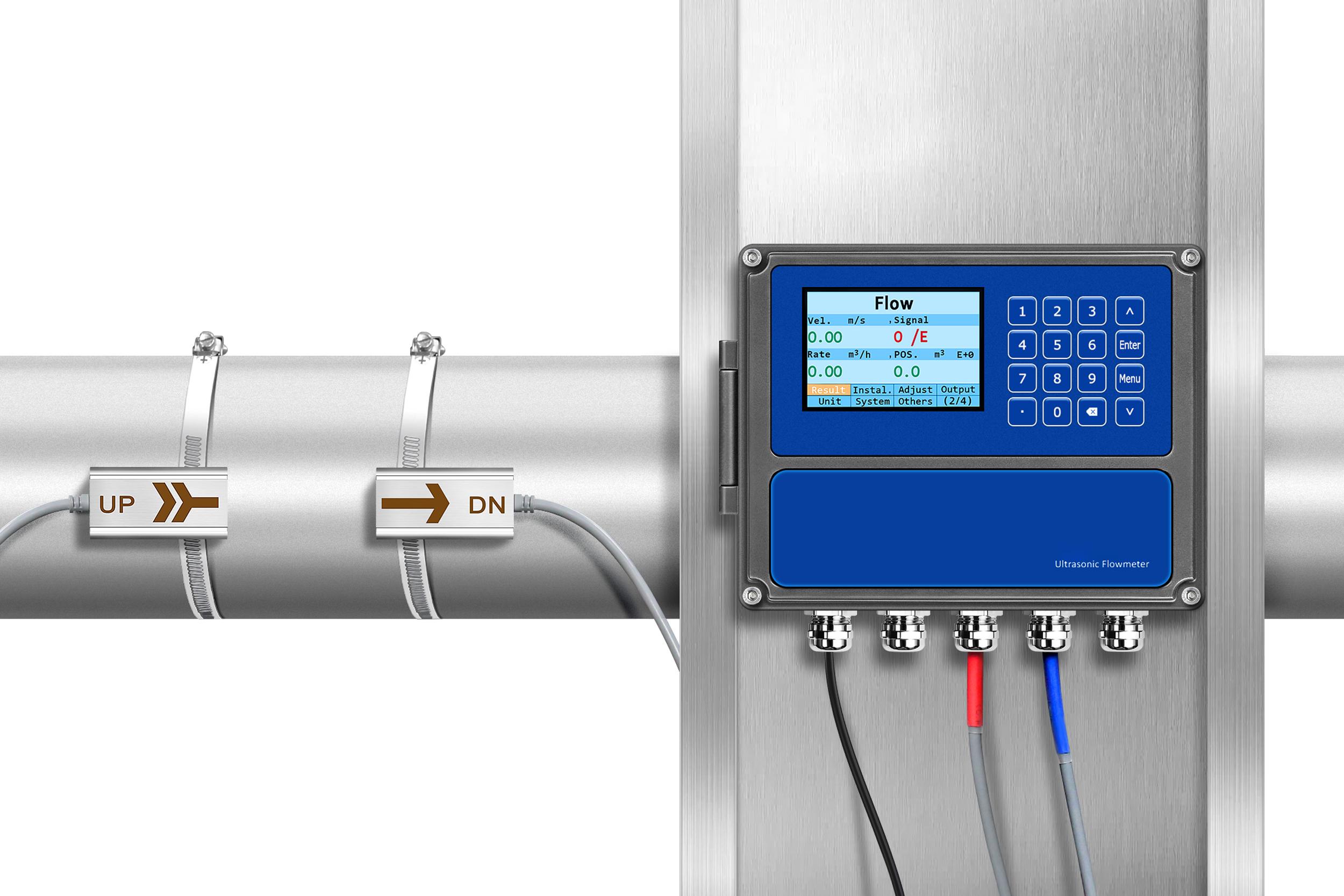
I’ve received countless calls from frustrated operators dealing with inaccurate flow readings.
Flow meter inaccuracy usually stems from improper installation, incorrect setup, process changes, or equipment damage. Systematic troubleshooting can identify and resolve these issues.

Flow Meter Troubleshooting Overview
Let me share my troubleshooting approach based on years of field experience.
What are the Causes for Inaccurate Flow Measurement?
Operators often struggle to identify the root cause of measurement errors.
Common causes include improper installation, pipe conditions, fluid properties changes, electronic issues, and environmental factors affecting meter performance.
From my diagnostic experience:
Primary Error Sources
Installation Issues
Problem Impact Solution Insufficient straight run Profile distortion Relocate meter Air pockets Signal loss Adjust orientation Poor mounting Signal weakness Proper installation Pipe condition Reading errors Surface preparation Process Conditions
- Fluid property changes
- Flow profile disturbances
- Temperature variations
- Pressure fluctuations
Environmental Factors
External Influences
- Vibration effects
- Temperature changes
- Electromagnetic interference
- Humidity impact
Maintenance Issues
- Buildup accumulation
- Sensor degradation
- Cable deterioration
- Software problems
How Do You Troubleshoot a Flow Meter?
Many technicians lack a systematic approach to flow meter troubleshooting.
Effective troubleshooting requires a step-by-step approach: checking installation, verifying settings, testing signals, and validating measurements.

Troubleshooting Steps Diagram
Based on my field experience:
Systematic Approach
Initial Assessment
Step Action Purpose Visual inspection Check physical setup Identify obvious issues Data analysis Review readings Spot patterns Signal check Verify strength Confirm transmission Parameter review Validate settings Ensure correctness Diagnostic Steps
- Installation verification
- Signal analysis
- Parameter validation
- Performance testing
Advanced Troubleshooting
Technical Analysis
- Waveform examination
- Noise evaluation
- Temperature effects
- Flow profile analysis
Documentation
- Error logging
- Parameter changes
- Test results
- Corrective actions
How to Tell if a Flow Meter is Bad?
Identifying a faulty flow meter can be challenging without proper knowledge.
Key indicators of a bad flow meter include erratic readings, zero signal strength, consistent errors after calibration, and failure to respond to flow changes.
Drawing from my diagnostic experience:
Warning Signs
Performance Indicators
Symptom Possible Cause Verification Method No signal Sensor failure Signal test Erratic readings Electronics issue Trend analysis Zero response System failure Flow validation Drift Calibration error Comparison test System Checks
- Signal quality
- Response time
- Repeatability
- Zero stability
Verification Methods
Testing Procedures
- Known flow testing
- Signal validation
- Zero flow check
- Comparison testing
Analysis Tools
- Diagnostic software
- Signal analyzers
- Data loggers
- Trend analysis
How to Calibrate a Flow Meter?
Proper calibration is crucial for accurate measurements.
Calibration involves zero-point adjustment, span verification, and signal optimization, typically requiring comparison with a reference standard.

Calibration Process Diagram
Based on my calibration experience:
Calibration Process
Preparation Steps
Step Action Purpose System check Verify conditions Ensure stability Zero flow Establish baseline Set reference point Parameter review Confirm settings Ensure accuracy Standard setup Reference preparation Enable comparison Calibration Steps
- Zero adjustment
- Span verification
- Linearity check
- Documentation
Quality Assurance
Validation Methods
- Multiple point testing
- Repeatability checks
- Error analysis
- Documentation review
Follow-up Actions
- Parameter updates
- Certificate generation
- Maintenance planning
- Record keeping
Conclusion
Accurate flow measurement requires proper installation, regular maintenance, systematic troubleshooting, and periodic calibration to ensure reliable operation and precise readings.